Figure 2.
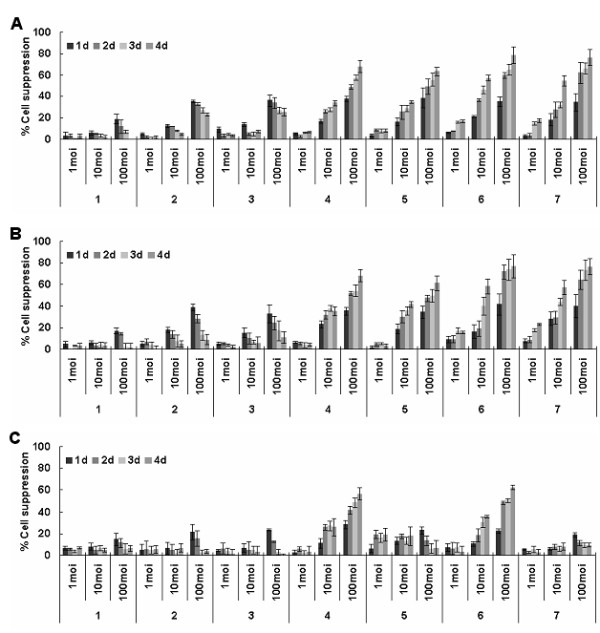
Assessment of the selective inhibition effect of Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin on melanoma cells. Effects of the different MOIs and infection times on (A), A375 cell viability, (B) B16 cell viability, and (C), on HEM cell viability. Cells were seeded in 96-well plates (1 × 104 cells/well) one day before cells were infected with various concentrations (1 MOI, 10 MOI, and 100 MOI) of the indicated adenoviruses. Tumor viability was measured every day over a 4 days period by MTT colorimetric assay and all measurements were performed in triplicate. Data are presented as mean ± SD. In normal HEM human epidermal melanocytes (C), infection with Ad-CMV-E1a or Ad-CMV-E1a-Apoptin, but not Ad-CMV-Apoptin, Ad-hTERT-Apoptin, Ad-hTERT-E1a, or Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin, induced growth inhibition. In contrast, in A375 (A) and B16 (B) melanoma cells, Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin, Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin, Ad-CMV-E1a, and Ad-hTERT-E1a infection resulted in significant growth inhibition. 1. Ad-mock; 2. Ad-CMV-Apoptin; 3. Ad-hTERT-Apoptin; 4. Ad-CMV-E1a; 5. Ad-hTERT-E1a; 6. Ad-CMV-E1a-Apoptin; 7. Ad-hTERT-E1a-Apoptin.
