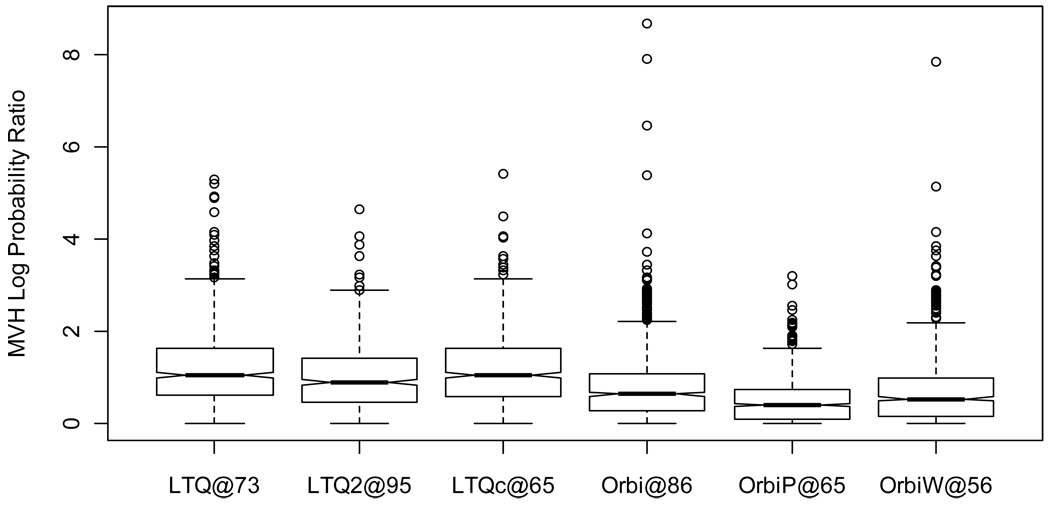
Figure 10. Study 5 yeast protein spectral count stability.
Spectral count differentiation attempts to detect differences between samples by recognizing changes in the numbers of spectra identified to those proteins. This image depicts the stability of spectral counts across six replicates when the sample is unchanged. A value of zero represents spectral counts that are spread across the replicates as evenly as possible. A value of 5 indicates that the ratio of probabilities for the observed spread of spectral counts versus the even distribution is e5=148. LTQs showed greater instability of spectral counts than did Orbitraps.