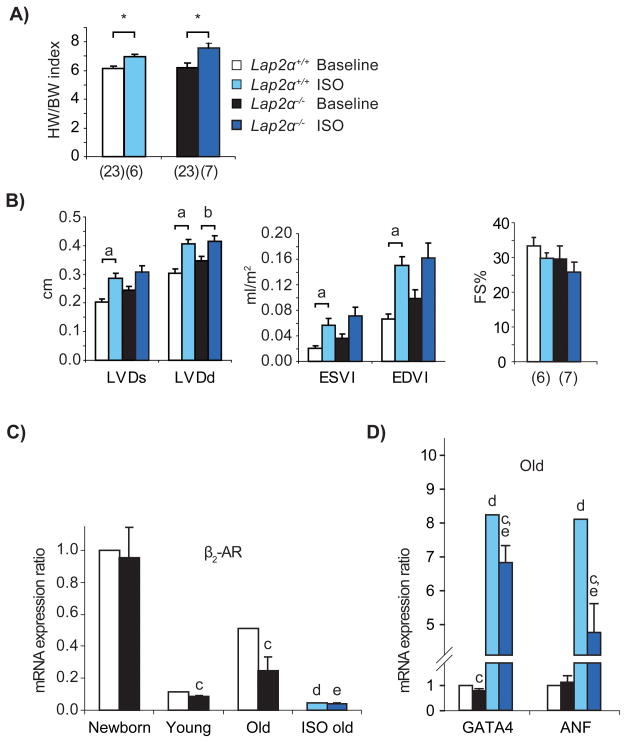
Figure 5. Lap2α−/− mice show a blunted response to chronic isoproterenol infusion.
A) Lap2α+/+ and Lap2α−/− male mice exhibit a similar increase in heart weight/body weight (HW/BW) indexes after 7 days of ISO treatment. (*p<0.05 ANOVA). B) Echocardiography reveals the absence of significant left ventricular chamber dilation in Lap2α−/− mice and preserved basal systolic function in both genotypes. [LVDd/s – left ventricular diameter in diastole/systole; ESVl – end-systolic left ventricular volume index; EDVl – end-diastolic left ventricular volume index; (n) - sample size. Data were analyzed using Student’s paired t-test (comparisons within one genotype before and after the treatment) and one way-ANOVA (comparisons between the two genotypes). (a) p<0.05, (b) p = 0.05]. C) Relative baseline mRNA levels of β2-AR are lower in Lap2α−/− hearts compared to WT, whereas ISO treatment causes its downregulation in both genotypes. D) ISO-induced increase in expression of fetal and pro-fibrotic genes is diminished in the absence of LAP2α. (qPCR analyses of heart tissue, n = 5 ISO-treated + 4 – 5 untreated male littermate pairs of each age; ANOVA, p<0.05 for (c) WT vs. KO of the respective age, (d) WT baseline vs. WT ISO-treated and (e) KO baseline vs. KO ISO-treated animals, mean ± SE).