Abstract
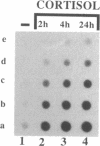
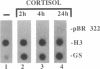
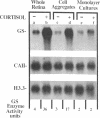
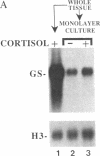
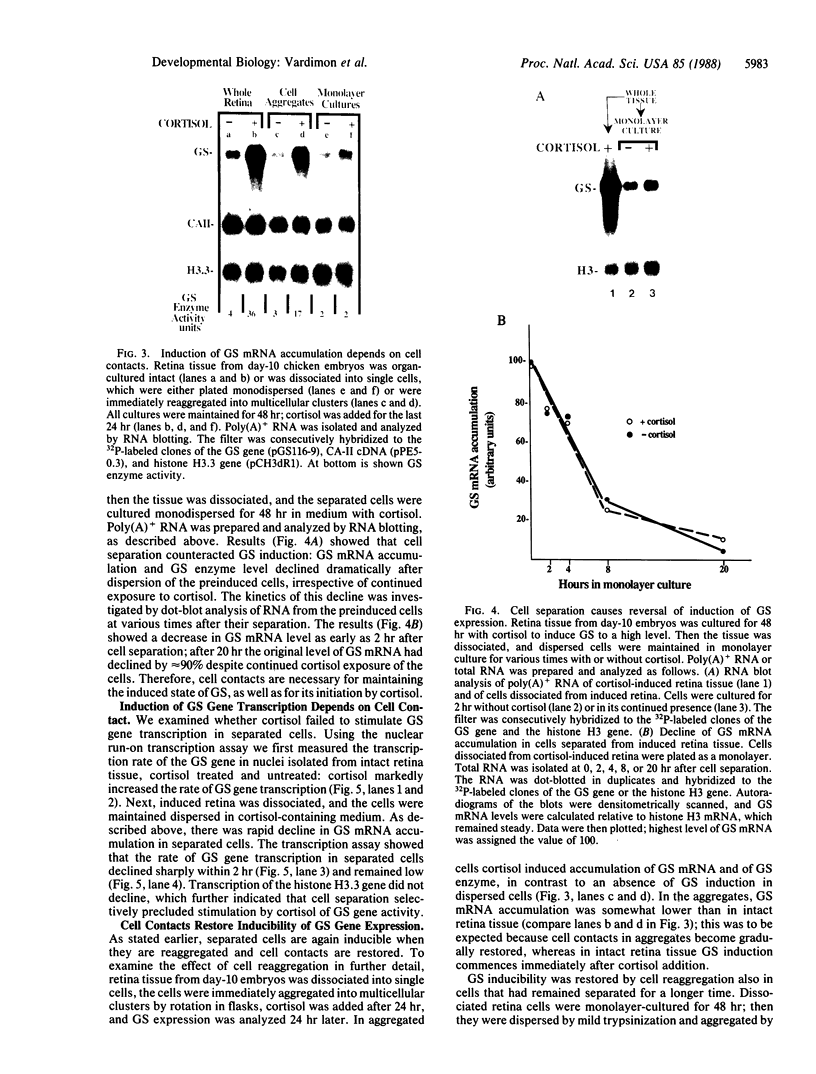
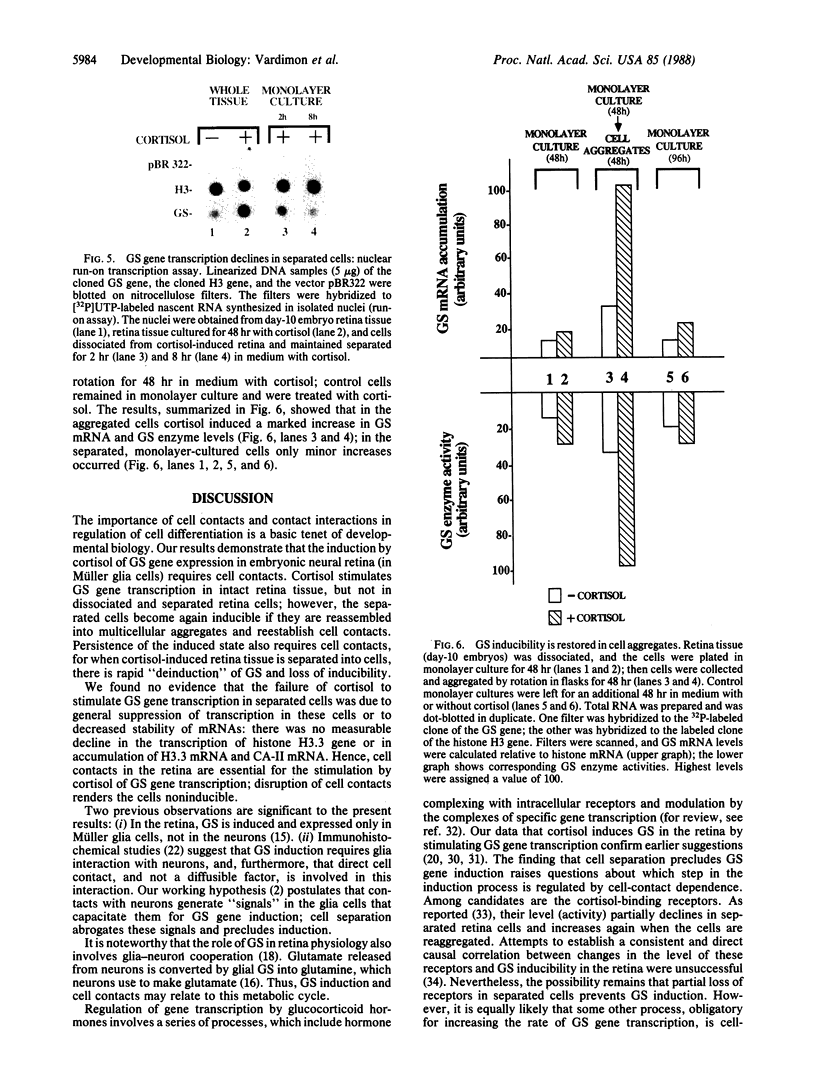
In embryonic neural retina the enzyme glutamine synthetase [GS; L-glutamate:ammonia ligase (ADP-forming), EC 6.3.1.2] is a glia-specific differentiation marker inducible with cortisol. We show that cortisol elicits GS mRNA accumulation by stimulating transcription of the GS gene and that this stimulation requires cell contacts: in dissociated and separated retina cells GS gene transcription was not induced; when the separated cells were reassembled into multicellular aggregates, restoring cell contacts, accumulation of GS mRNA was again inducible. In cells dissociated from retina tissue that had been preinduced with cortisol, GS gene transcription rapidly declined, despite continued hormone availability. In the separated cells transcription of the histone H3.3 gene and accumulation of carbonic anhydrase II mRNA were unaffected; therefore, cell separation selectively precluded induction of the GS gene. These findings provide direct evidence for the regulatory role of cell contacts in hormonal control of gene transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson A., Rutishauser U. Neural cell adhesion molecule regulates cell contact-mediated changes in choline acetyltransferase activity of embryonic chick sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):479–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Farmer S. R., Penman S. Protein synthesis requires cell-surface contact while nuclear events respond to cell shape in anchorage-dependent fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Robinson G. S., Bucher N. L., Farmer S. R. Cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions differentially regulate the expression of hepatic and cytoskeletal genes in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2161–2165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew H., Attwell D. Electrogenic glutamate uptake is a major current carrier in the membrane of axolotl retinal glial cells. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):707–709. doi: 10.1038/327707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dony C., Kessel M., Gruss P. Post-transcriptional control of myc and p53 expression during differentiation of the embryonal carcinoma cell line F9. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):636–639. doi: 10.1038/317636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B. A chicken histone H3 gene contains intervening sequences. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):434–436. doi: 10.1038/297434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy A. J., Voaden M. J., Marshall J. Glutamate metabolism in the frog retina. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):50–52. doi: 10.1038/252050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. L., Aggeler J., Farson D. A., Hatier C., Hassell J., Bissell M. J. Influence of a reconstituted basement membrane and its components on casein gene expression and secretion in mouse mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):136–140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Moscona A. A. Hormonal induction of glutamine synthetase in cultures of embryonic retina cells: requirement for neuron-glia contact interactions. Dev Biol. 1983 Apr;96(2):529–534. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Moscona A. A. Induction of glutamine synthetase in embryonic neural retina: localization in Müller fibers and dependence on cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Bozzaro S., Landfear S., Lodish H. F. Cell--cell contact, cyclic AMP, and gene expression during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:117–154. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60581-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Linser P. Developmental and experimental changes in retinal glia cells: cell interactions and control of phenotype expression and stability. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:155–188. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60582-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Moscona M. H., Saenz N. Enzyme induction in embryonic retina: the role of transcription and translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Shirayoshi Y., Okazaki K., Yasuda K., Takeichi M. Transformation of cell adhesion properties by exogenously introduced E-cadherin cDNA. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):341–343. doi: 10.1038/329341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patejunas G., Young A. P. Tissue-specific regulation of avian glutamine synthetase expression during development and in response to glucocorticoid hormones. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1070–1077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M. Steroid hormone regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:529–566. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad A. D., Moscona A. A. Cortisol receptors and inducibility of glutamine synthetase in embryonic retina. Cell Differ. 1985 Jun;16(4):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(85)90574-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad A. D., Soh B. M., Moscona A. A. Modulation of cortisol receptors in embryonic retina cells by changes in cell-cell contacts: correlations with induction of glutamine synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):701–708. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Jamrich M., Dawid I. B. Cell interactions and the control of gene activity during early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;114(1):238–246. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soh B. M., Sarkar P. K. Control of glutamine synthetase messenger RNA by hydrocortisone in the embryonic chick retina. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):316–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar F., Geiger B., Ben-Ze'ev A. Cell contact- and shape-dependent regulation of vinculin synthesis in cultured fibroblasts. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):787–791. doi: 10.1038/319787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Fox L. E., Moscona A. A. Accumulation of c-src mRNA is developmentally regulated in embryonic neural retina. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4109–4111. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Fox L. E., Moscona A. A. Developmental regulation of glutamine synthetase and carbonic anhydrase II in neural retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9060–9064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara C. M., Federspiel M., Dodgson J. B. Isolation of the chicken carbonic anhydrase II gene. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:332–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]