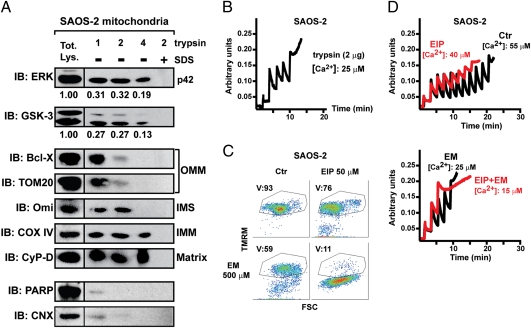
Fig. 3.
A fraction of ERK and of GSK-3 is located in mitochondria, and ERK inhibition sensitizes SAOS-2 cells to mitochondrial depolarization and PTP opening. (A) Isolated mitochondria (70 μg per point) were treated for 1 h with the reported quantities of trypsin (in micrograms; trypsin concentration: 5, 10, or 20 μg/mL) and analyzed by Western immunoblot (IB). Where indicated, 0.1% SDS was added before trypsin. Blots were probed for ERK and GSK-3; and for a panel of mitochondrial markers of the outer and inner membrane (OMM and IMM, respectively), of the intermembrane space (IMS), and of the matrix. COX-IV is a cytochrome oxidase subunit. Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) was used as an example of a non-mitochondrial soluble protein; and calnexin (CNX) as an endoplasmic reticulum marker. Densitometry analyzes ERK or GSK-3 levels. (B) Ca2+ uptake in trypsin-treated mitochondria was assessed by Calcium Green-5N fluorescence. Because the probe does not permeate mitochondria, Ca2+ entering viable organelles is displayed by a rapid decrease of the fluorescence spike after administration to the cells of subsequent Ca2+ pulses (5 μM each). The final increase in fluorescence indicates pore opening. (C) FACS analysis [forward scatter (FSC) vs. TMRM] showing mitochondria depolarization in cells exposed to EM20-25 (EM) for 1 h with or without a 30-min preincubation with EIP. The percentage of viable cells (V, TMRM positive, in the quadrant) is reported. (D) PTP opening was measured as in B, but on whole cells. Treatment with ERK inhibitor peptide (EIP) (5 μM, in red) decreased the number of spikes before the permeability transition occurred, either in control conditions or when cells were incubated with EM20-25 (EM, 50 μM).