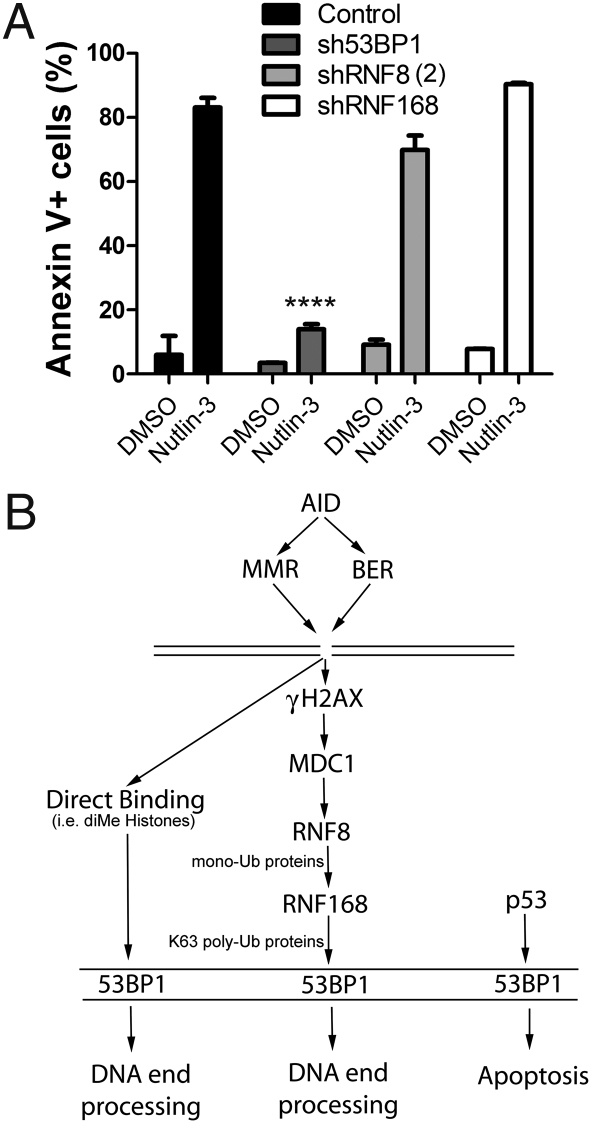
Fig. 4.
53BP1 knockdown cells, but not RNF8/168 knockdown cells, are resistant to Nutlin-3–mediated apoptosis. (A) Percentage of control, sh53BP1, shRNF8(2), and shRNF168 CH12F3-2 cells undergoing apoptosis (i.e., surface annexin V+) after treatment with Nutlin-3 or DMSO for 1 day. Each assay was carried out with two different clones of each population. Statistical significance was tested by two-way ANOVA. ****P <.0001. (B) Schematic illustrating two different roles for 53BP1. AID indirectly induces a DSB by the actions of the mismatch repair (MMR) and base excision repair (BER) pathways. 53BP1 is recruited to the DNA DSB site either by direct binding (via the MRN complex or dimethylated histones) or through the γH2AX-RNF8-RNF168 amplification pathway, the latter of which leads to the accumulation and stabilization of 53BP1 at the break site. These pathways ultimately lead to end-processing and resolution of the DNA break. Independent of the RNF8/168 cascade, 53BP1 could lead to p53 stabilization or enhanced transcriptional activity in response to apoptosis signaling.