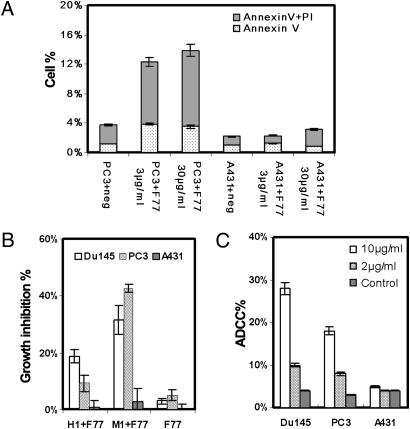
Fig. 3.
Effects of mAb F77 on prostate cancer cells in vitro. (A) Apoptosis assay by Annexin V and propidium iodide staining. Bars indicate percentages of cells stained with Annexin V and propidium iodide. A431 and PC3 cells were treated with 3 or 30 μg/mL mAb F77 for 4 h at 37°C. (B) MTT assay with 25 μg/mL mAb F77 in 100 μL medium containing 1% human serum (H1+F77) and 25 μg/mL mAb F77 in 100 μL medium containing 1% mouse serum (M1+F77). Cell viability was measured by standard MTT assay. Growth inhibition %, [(control wells − treated wells) / control wells] × 100. Growth inhibition percentage increased in response to the addition of either mouse or human serum, indicating mAb F77 induced CDC. (C) ADCC assay: PC3 or Du145 target cells were treated with different concentrations of mAb F77 (0, 2, and 10 μg/mL) at an effector-to-target cell ratio of 2:1. A431 cells were used as control cells. ADCC percentage calculation followed the instruction from a CytoTox 96 nonradioactive cytotoxicity assay (Promega). Negative controls are cells treated with an irrelevant murine IgG3 mAb. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of triplicate measurements.