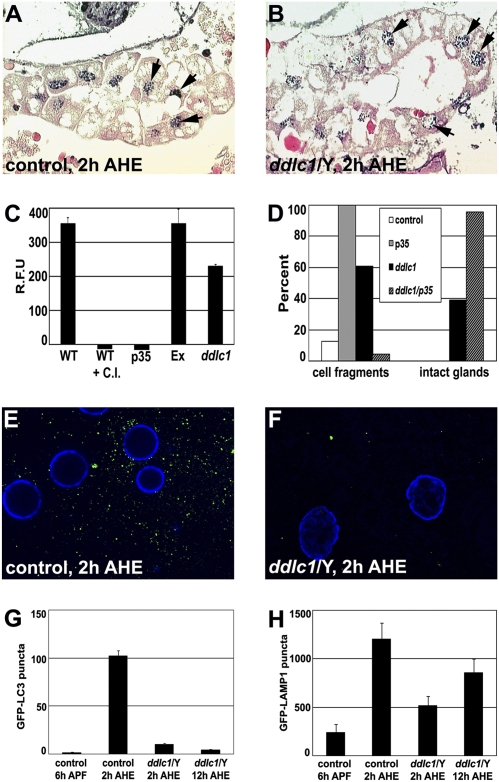
Fig. 2.
ddlc1 mutants have altered caspase activity and autophagy. (A and B) TUNEL assay to detect DNA fragmentation (arrows) in control (A) and ddlc1 mutant (B) salivary glands 2 h AHE (n = 5 animals/genotype). (C) Average caspase activity (±SEM) of pupal lysates collected 4 h after puparium formation and measured by cleavage of fluorogenic caspase-3 substrate Z-DEVD-AMC (n = 3). WT, wild-type Canton S; WT + C.I., Canton S + caspase inhibitor DEVD-CHO; p35, daGAL4 × uas-p35: Ex, precise excision of the P element; ddlc1, ddlc1/Y. (D) Percent animals with salivary gland cell fragments and intact glands in paraffin sections of pupae 12 h AHE. Genotypes: Control (fkhGAL4/+) (n = 16), p35 (fkhGAL4/uas-p35) (n = 13), ddlc1 mutant (ddlc1/Y) (n = 28), and p35 expression in ddlc1 mutant (ddlc1/Y; fkhGAL4/uas-p35) (n = 24). (E and F) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of salivary glands expressing GFP-LC3 (green) and DNA (blue). (E) Control (P-excision; +/+; fkhGAL4/uas-GFP-LC3) salivary glands have large numbers of puncta 2 h AHE (n = 20 glands). (F) ddlc1 mutant (ddlc1/Y; +/+; fkhGAL4/uas-GFP-LC3) salivary glands have few puncta 2 h AHE (n = 17 glands). (G) Average number of GFP-LC3 puncta (±SEM) in the genotypes shown in E and F and in ddlc1 mutant salivary glands 12 h AHE (n = 23 glands). (H) Average number of GFP-LAMP1 puncta (±SEM) in salivary glands of control (P-excision; +/+; +/tub-GFP-LAMP1) 6 h after puparium formation, 2 h AHE, and in ddlc1 mutant (ddlc1/Y; +/+; +/tub-GFP-LAMP1) 2 h AHE, and 12 h AHE (n = 21 glands).