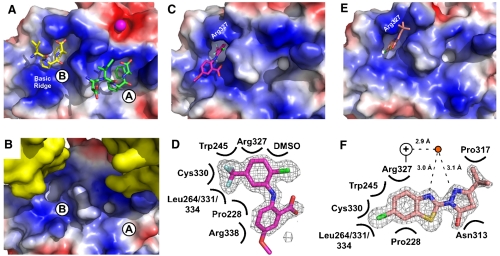
Fig. 3.
Crystal structures of CFAM and BCBP bound to E. coli ExoI. (A) Crystal structure of E. coli ExoI bound to two SSB-Ct peptides (4). Biochemical experiments have shown that only the A site is used for SSB/ExoI association in solution; the B site is likely an artifact of high peptide concentrations used in crystallization (4). ExoI surface is stained according to electrostatics (Blue, electropositive; Red, electronegative; White, neutral) and peptides are colored by atoms. A bound Mg2+ ion is shown as a magenta sphere. (B) Crystal packing in apo-ExoI protein crystals. A symmetrically-related ExoI molecule (Yellow) binds to the SSB-Ct peptide-binding surface of an adjacent ExoI molecule, distorting the hydrophobic pocket that accommodates the SSB-Ct peptide in the A site but not the B site. (C) Crystal structure of CFAM bound to ExoI. ExoI is colored as in A and CFAM is colored by atoms (Magenta, carbon; Red, oxygen; Blue, nitrogen; Green, chlorine; Pale Blue, fluorine). (D) Contact map depicting ExoI residues and solution components that contact CFAM. Omit Fo-Fc electron-density contoured at 2.8σ is shown for CFAM. (E) Crystal structure of BCBP bound to ExoI. ExoI is colored as in A and BCBP is colored by atoms (Pink, carbon; Red, oxygen; Blue, nitrogen; Green, chlorine; Yellow, sulfur). (F) Contact map depicting ExoI residues and solution components that contact BCBP. Omit Fo-Fc electron-density contoured at 2.8σ is shown for BCBP. Distances between a water molecule (Red Circle) and BCBP and the closest nitrogen from the Arg327 guanidino group (+) are provided. All figures were made by using Pymol (20).