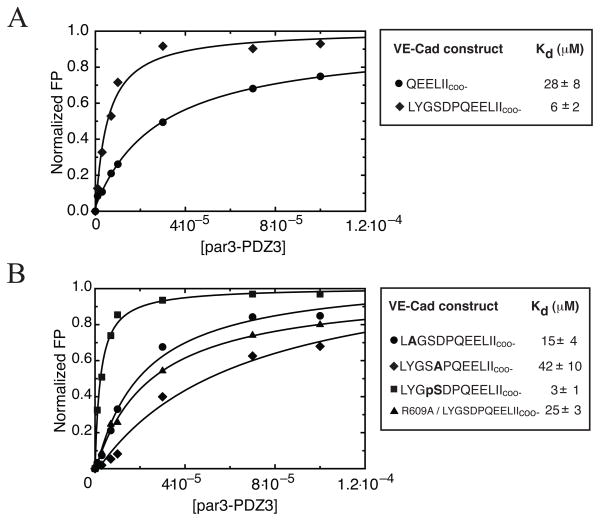
Figure 3.
A) Determination of affinity for different length VE-Cad peptides binding to par3-PDZ3 using a fluorescence polarization assay. All peptides contained n-terminally linked rhodamine label. Comparison of binding curves of short (●) and long (◆) constructs of VE-Cad revealed a ~5-fold increase in binding affinity for the longer VE-Cad segment. B) Comparison of binding curves generated for YtoA (●) and DtoA (◆) VE-Cad mutants revealed that P−7(D) contributes to VE-Cad interaction with par3-PDZ3 as indicated by the decrease in binding affinity. Mutation R609A of par3-PDZ3 (▲) shows decrease in binding affinity when titrated against long VE-Cad construct. Further modification of VE-Cad by phosphorylation of P−8(S) (■) revealed that additional negative charge introduced to distal amino acids can increase binding relative to the long construct by ~2-fold. Bold letters signify location of alanine substitutions or serine phosphorylation (pS). Error in Kd is estimated from fitting.