Figure 1.
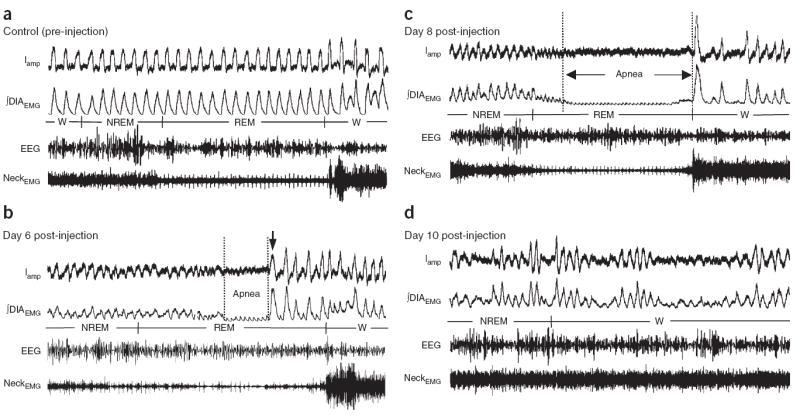
Breathing pattern is progressively disrupted, initially during sleep and then also during wakefulness. (a) Pre-injection, breathing is regular during sleep and wakefulness (W). (b) Post-injection, hypopnea and short central apneas (note the absence of ∫DIAEMG) occur initially during REM sleep. At day 6, at the end of the REM-associated apnea, a number of small breaths precede awakening (arrow). (c) Hypopnea and short central apneas subsequently increase in frequency and duration during NREM and REM sleep (day 8; Supplementary Video 1) and also during wakefulness. (d) Ultimately, an ataxic breathing pattern develops (day 10). Iamp: inspiratory amplitude. ∫DIAEMG: integrated diaphragm EMG. NeckEMG: dorsal neck EMG. EEG: electroencephalogram. Scale bar, 2 s. See Supplementary Figures 2–6 for continuous 5-min data recordings.
