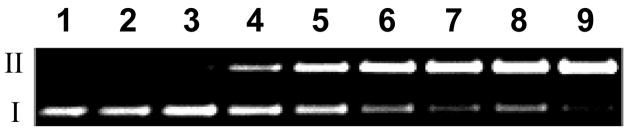
Figure 1.
DNA cleavage by various concentrations of reductively-activated 5 under anaerobic conditions. Supercoiled plasmid DNA (33 μg/mL, pGL-2 Basic) was incubated with 5 (25–150 μM), NADPH (500 μM), cytochrome P450 reductase (0.03 mU/μL), catalase (100 μg/mL), superoxide dismutase (10 μg/mL), sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0), and desferal (1 mM) under anaerobic conditions at 25 °C for 4 h, followed by agarose gel electrophoretic analysis. Lane 1, DNA alone (S = 0.19 ± 0.02); lane 2, NADPH (500 μM) + reductase (0.03 mU/μL) (S = 0.2 ± 0.01); lane 3, 5 (150 μM) (S = 0.18 ± 0.03); lanes 4–9, NADPH (500 μM) + reductase (0.03 mU/μL) + 5 (25 μM, lane 4) (S = 0.46 ± 0.11); (50 μM, lane 5) (S = 0.71 ± 0.1); (75 μM, lane 6) (S = 0.81 ± 0.08); (100 μM, lane 7) (S = 1.13 ± 0.11); (125 μM, lane 8) (S = 1.22 ± 0.01); (150 μM, lane 9) (S = 1.46 ± 0.03). The values, S, represent the mean number of strand breaks per plasmid molecule and were calculated using the equation S = −ln fI, where fI is the fraction of plasmid present as in the supercoiled form I.