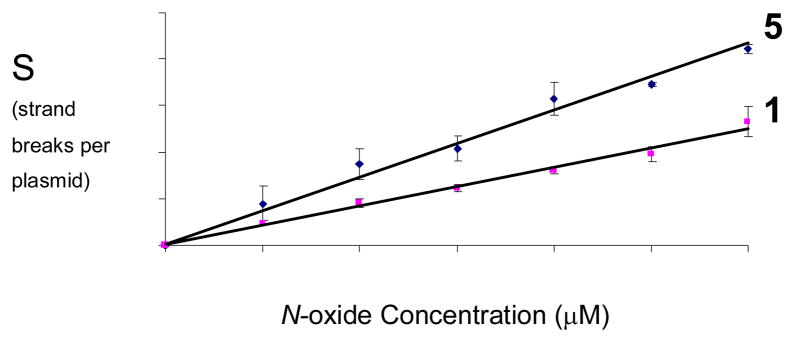
Figure 3.
Comparison of the efficiency of redox-activated DNA-cleavage by 5 and TPZ under anaerobic conditions. Supercoiled plasmid DNA (33 μg/mL, pGL-2 Basic) was incubated with TPZ or 5 (25–150 μM), NADPH (500 μM), cytochrome P450 reductase (0.03 mU/μL), catalase (100 μg/mL), superoxide dismutase (10 μg/mL), sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0), and desferal (1 mM) under anaerobic conditions at 24 °C for 4 h, followed by agarose gel electrophoretic analysis. The values, S, are derived from agarose gel data such as that shown in Figures 1 and 2 and represent the mean number of strand breaks per plasmid molecule and were calculated using the equation S = −ln fI, where fI is the fraction of plasmid present as form I. Background cleavage in the untreated plasmid was subtracted to allow direct comparison of DNA strand cleavage yields between different experiments.