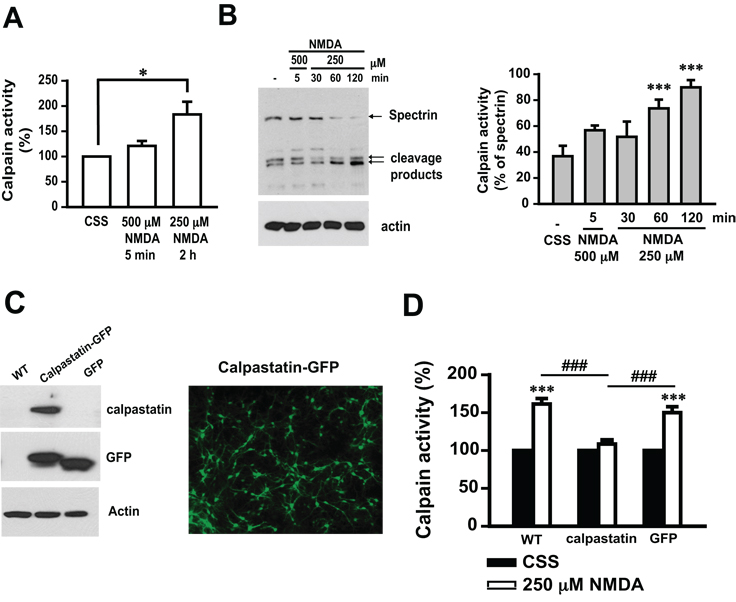
Fig. 2. NMDA treatment induces calpain activation in cortical neurons.
A, Fluorogenic analysis of calpain activity was performed in the whole cell lysate from cells treated with Controlled Salt Solution (CSS) or NMDA under the indicated conditions. The calpain activity in control cells treated with CSS only is regarded as 100%. B, Spectrin immunoblotting analysis (left) was performed on whole cell lysate from cells treated with 500 µM or 250 µM NMDA for the indicated times. Arrows indicate full-length spectrin (240 kDa) and calpain-dependent cleavage products (150 and 145 kDa). The calpain activity is quantified and presented as the percentage of cleavage products in total spectrin (right). n = 8. C, The expression of calpastatin and/or GFP in cortical neurons was assessed by immunoblotting (left) and fluorescence microscopy (right). For immunoblotting, whole cell lysate was prepared from cells transduced with Ad.calpastatin or Ad.GFP for 48 h. D, Calpastatin inhibited calpain activity induced by NMDA (250 µM for 2 h). Data shown in A, B and D represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05 as compared with cells treated with CSS, ### p < 0.001 as compared with cells treated with NMDA.