Abstract
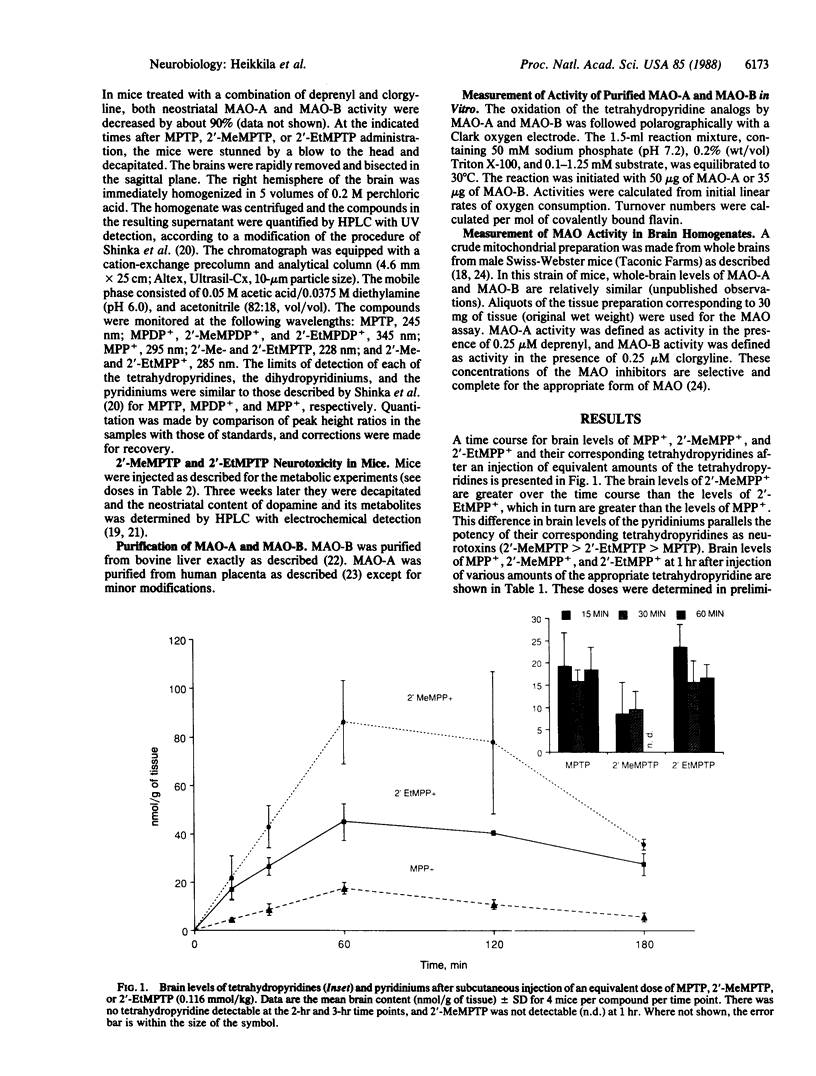
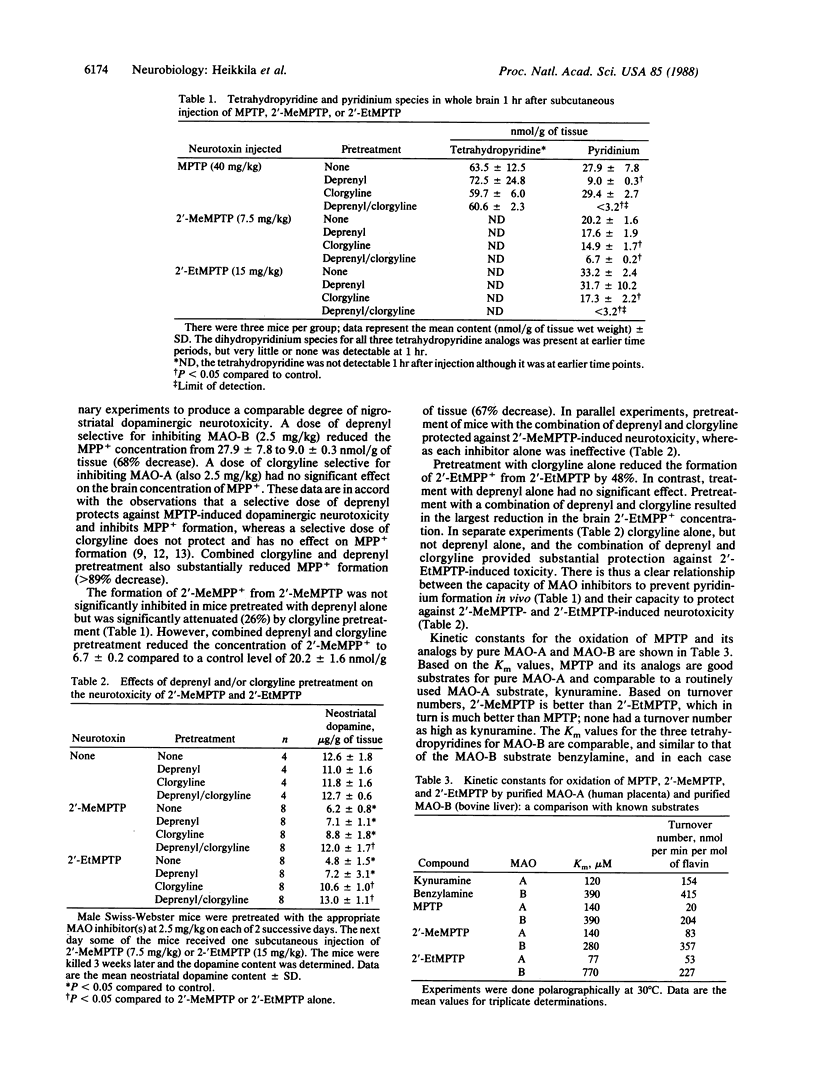
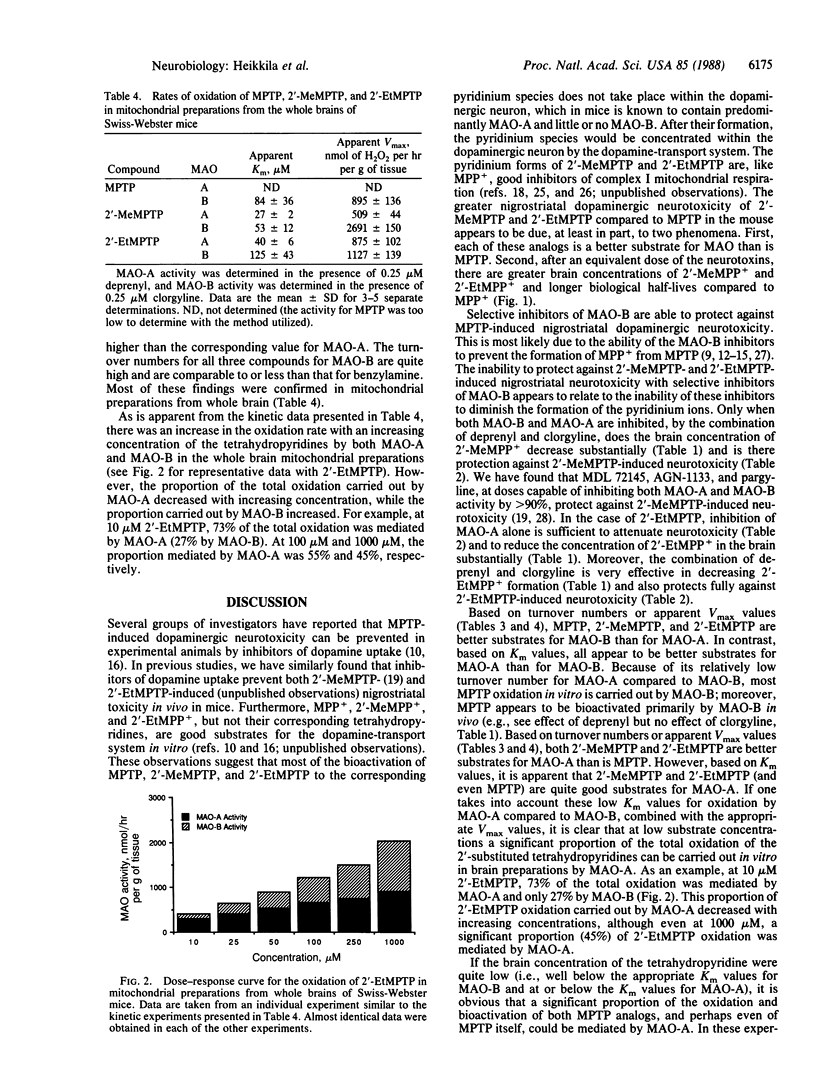
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is a potent dopaminergic neurotoxin that causes biochemical, pharmacological, and pathological deficits in experimental animals similar to those seen in human parkinsonian patients. All of the deficits can be prevented by treating mice with selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B), including deprenyl, prior to MPTP administration. We now report that the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of two potent MPTP analogs, namely the 2'-methyl and 2'-ethyl derivatives (2'-MeMPTP and 2'-EtMPTP), cannot be prevented by deprenyl pretreatment. However, the neurotoxicity of these two analogs can be prevented by pretreatment with a combination of deprenyl and the selective MAO-A inhibitor clorgyline at doses that are sufficient to almost completely inhibit both MAO-B and MAO-A activities. Moreover, the neurotoxicity of 2'-EtMPTP (but not of 2'-MeMPTP and MPTP) can be significantly attenuated by clorgyline alone. There was a parallel between the capacity of the MAO inhibitors to decrease the brain content of the pyridinium species after administration of the tetrahydropyridines and the capacity of the MAO inhibitors to protect against the neurotoxic action of the tetrahydropyridines. The data support the conclusion that both 2'-MeMPTP and 2'-EtMPTP are bioactivated to pyridinium species to a significant extent by MAO-A. Further, it appears that the formation of the pyridinium species plays an important role in the neurotoxic process.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burns R. S., Chiueh C. C., Markey S. P., Ebert M. H., Jacobowitz D. M., Kopin I. J. A primate model of parkinsonism: selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra by N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4546–4550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. S., Markey S. P., Phillips J. M., Chiueh C. C. The neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the monkey and man. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):166–168. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100046345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Peterson L. A., Castagnoli K. P., Trevor A. J., Castagnoli N., Jr Studies on the molecular mechanism of bioactivation of the selective nigrostriatal toxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Drug Metab Dispos. 1985 May-Jun;13(3):342–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Trevor A. J., Castagnoli N., Jr Active uptake of MPP+, a metabolite of MPTP, by brain synaptosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1228–1232. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Trevor A., Castagnoli N., Jr Metabolism of the neurotoxic tertiary amine, MPTP, by brain monoamine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):574–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. C., Williams A. C., Markey S. P., Ebert M. H., Caine E. D., Reichert C. M., Kopin I. J. Chronic Parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues. Psychiatry Res. 1979 Dec;1(3):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(79)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Hemrick-Luecke S. K. Persistent depletion of striatal dopamine in mice by m-hydroxy-MPTP. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;53(2):167–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R. E., Manzino L., Cabbat F. S., Duvoisin R. C. Protection against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):467–469. doi: 10.1038/311467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R. E., Sonsalla P. K. The use of the MPTP-treated mouse as an animal model of parkinsonism. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;14(3 Suppl):436–440. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R. E., Youngster S. K., Manzino L., Cabbat F. S., Duvoisin R. C. Effects of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine and related compounds on the uptake of [3H]3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine and [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine in neostriatal synaptosomal preparations. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):310–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitch J. A., D'Amato R. J., Strittmatter S. M., Snyder S. H. Parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin, N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6 -tetrahydropyridine: uptake of the metabolite N-methyl-4-phenylpyridine by dopamine neurons explains selective toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2173–2177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston J. W., Ballard P., Tetrud J. W., Irwin I. Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):979–980. doi: 10.1126/science.6823561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston J. W., Forno L. S., Rebert C. S., Irwin I. Selective nigral toxicity after systemic administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyrine (MPTP) in the squirrel monkey. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 6;292(2):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90777-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston J. W., Irwin I., Langston E. B., Forno L. S. Pargyline prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in primates. Science. 1984 Sep 28;225(4669):1480–1482. doi: 10.1126/science.6332378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey S. P., Johannessen J. N., Chiueh C. C., Burns R. S., Herkenham M. A. Intraneuronal generation of a pyridinium metabolite may cause drug-induced parkinsonism. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):464–467. doi: 10.1038/311464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. A., Kindt M. V., Heikkila R. E. Prevention of the nigrostriatal toxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine by inhibitors of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine transport. J Neurochem. 1986 Oct;47(4):1073–1079. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas W. J., Youngster S. K., Kindt M. V., Heikkila R. E. MPTP, MPP+ and mitochondrial function. Life Sci. 1987 Feb 23;40(8):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. R., Salach J. I., Singer T. P. Uptake of the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine (MPP+) by mitochondria and its relation to the inhibition of the mitochondrial oxidation of NAD+-linked substrates by MPP+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):743–748. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricaurte G. A., Langston J. W., DeLanney L. E., Irwin I., Brooks J. D. Dopamine uptake blockers protect against the dopamine depleting effect of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in the mouse striatum. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Sep 6;59(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salach J. I., Singer T. P., Castagnoli N., Jr, Trevor A. Oxidation of the neurotoxic amine 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) by monoamine oxidases A and B and suicide inactivation of the enzymes by MPTP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):831–835. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90614-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salach J. I., Weyler W. Iron content and spectral properties of highly purified bovine liver monoamine oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinka T., Castagnoli N., Jr, Wu E. Y., Hoag M. K., Trevor A. J. Cation-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography assay for the nigrostriatal toxicant 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine and its monoamine oxidase B generated metabolites in brain tissues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jul 10;398:279–287. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96513-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., D'Amato R. J. MPTP: a neurotoxin relevant to the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. The 1985 George C. Cotzias lecture. Neurology. 1986 Feb;36(2):250–258. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonsalla P. K., Heikkila R. E. The influence of dose and dosing interval on MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 7;129(3):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90444-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonsalla P. K., Youngster S. K., Kindt M. V., Heikkila R. E. Characteristics of 1-methyl-4-(2'-methylphenyl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Sep;242(3):850–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström E., Jonsson G. Pharmacological interference with the neurotoxic action of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) on central catecholamine neurons in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 16;110(3):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90555-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngster S. K., Sonsalla P. K., Heikkila R. E. Evaluation of the biological activity of several analogs of the dopaminergic neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. J Neurochem. 1987 Mar;48(3):929–934. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



