Figure 2.
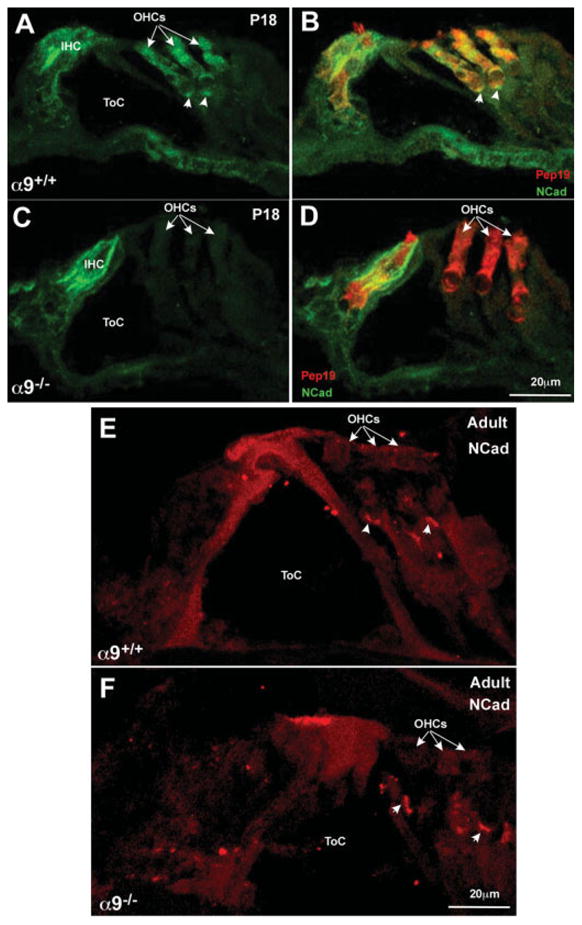
N-Cadherin immunostaining reveals loss of expression in OHCs in the α9 null mice. (A) Immunostaining for N-Cadherin (green) in wild-type P18 cochleae reveals expression primarily in the hair cells of the organ of Corti. (B) Double labeling the hair cells with Pep19 (red) reveals the extent of the hair cell boundary and that the hair cells do express N-Cadherin. (C) Immunostaining for N-Cadherin in P18 α9 null cochleae reveals expression in IHCs, but not in the OHC region (OHCs indicated by arrows). (D) Double labeling the section with Pep19 (red) reveals the coexistence of Pep19 and N-Cadherin in the IHC, but the OHCs do not express N-Cadherin, and remain fluorescent in red only. (E) In adults, N-Cadherin (red) is expressed predominantly in the OHC region, and denser staining can be observed at the basal (synaptic) pole of the cells (arrowheads). (F) In the α9 nulls, N-Cadherin staining is similar to that observed in the wild-type OHCs, but the staining near the synaptic pole of the cells is brighter and the immunopositive plaque is large than observed in the wild-type mice.
