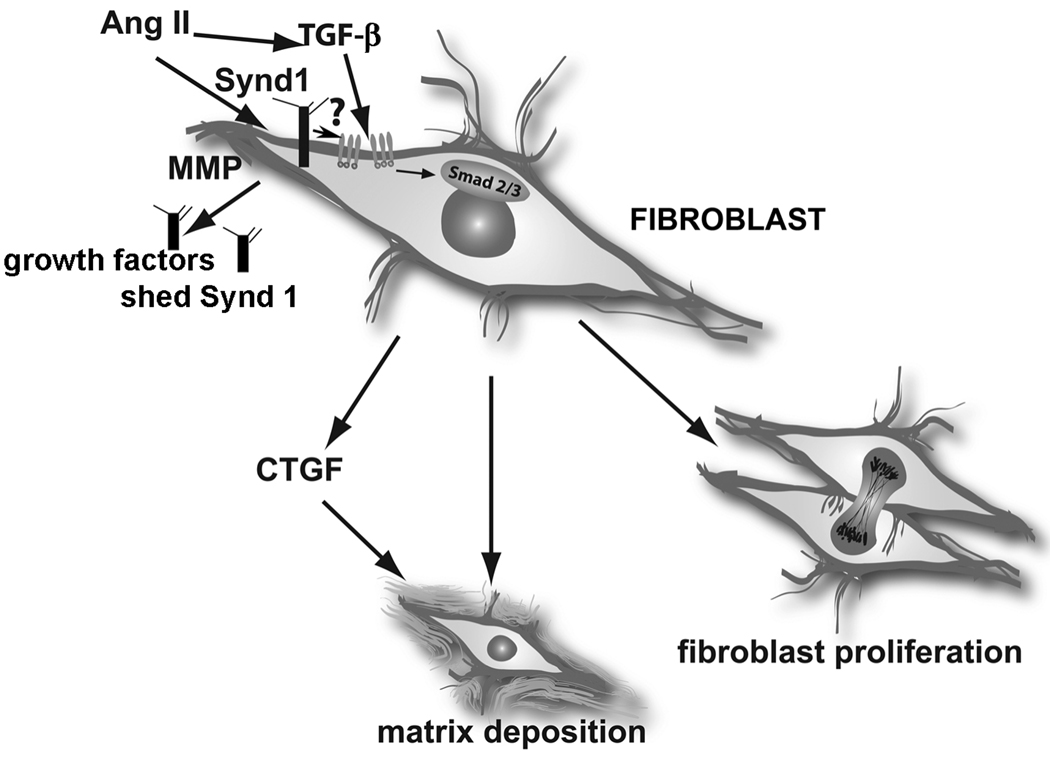
Figure.
The role of Syndecan-1 (Synd1) in cardiac fibrosis. Synd1 may act by presenting growth factors to their receptors, may increase TGF-β receptor levels, may promote TGF-β activation, or may activate downstream TGF-β signaling pathways. Understanding the role of syndecan-1 in cardiac injury is complicated by the possible presence of shed ectodomains (released due to increased Matrix Metalloproteinase [MMP] activity), that may sequester growth factors, or promote chemotactic gradients (Ang II, angiotensin II).