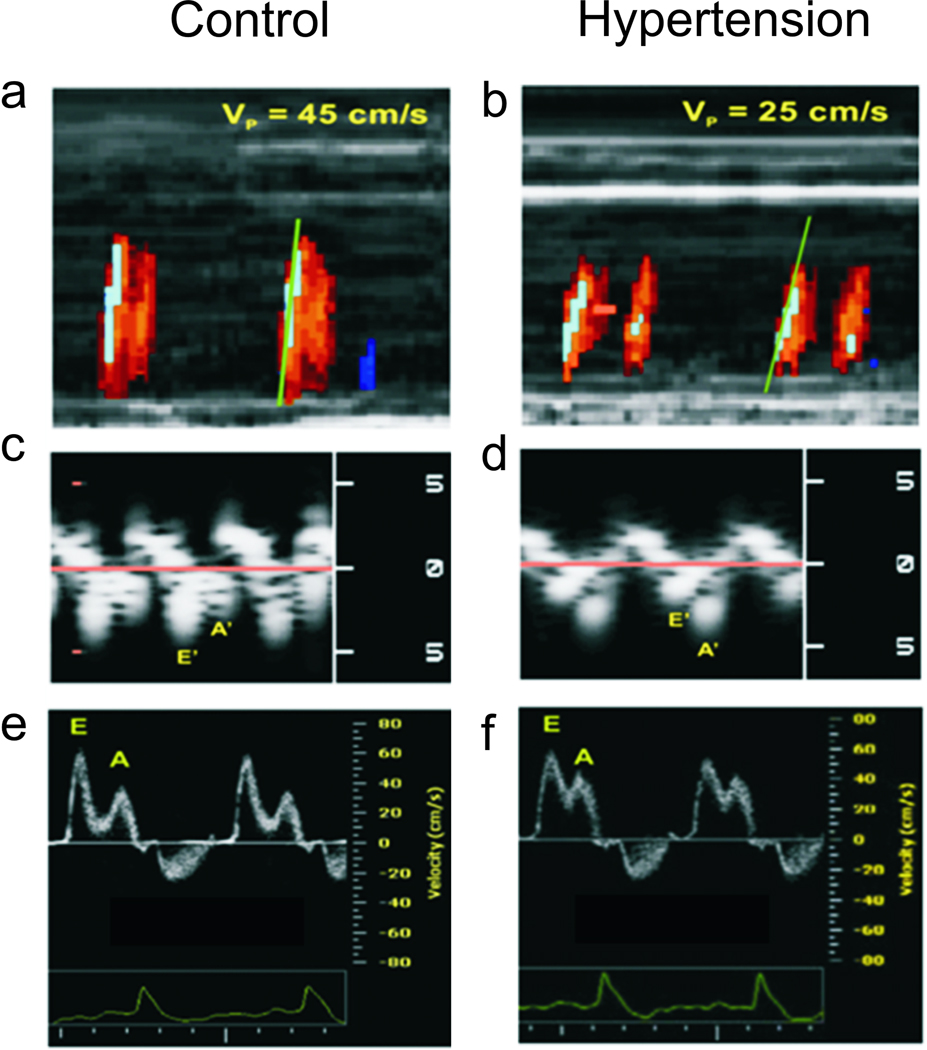
Figure 1.
Representative echocardiographic assessments of LV diastolic function.Panels a and b: Left ventricular inflow propagation velocity (Vp) interrogated with color M-mode Doppler. A control mouse shows a steeper isovelocity line slope, corresponding to a higher Vp compared with a hypertensive DOCA mouse. Panels c and d: Septal mitral annulus velocities interrogated with tissue Doppler imaging (TDI). The control animal has a higher E’ (early diastolic velocity), and lower A’ (late diastolic velocity) than the hypertensive animal. Panels e and f: Conventional pulsed wave Doppler shows a normal E/A (early to late diastolic filling velocity ratio) of >1 and <2 for both the control and DOCA mice, a pseudonormal” pattern.