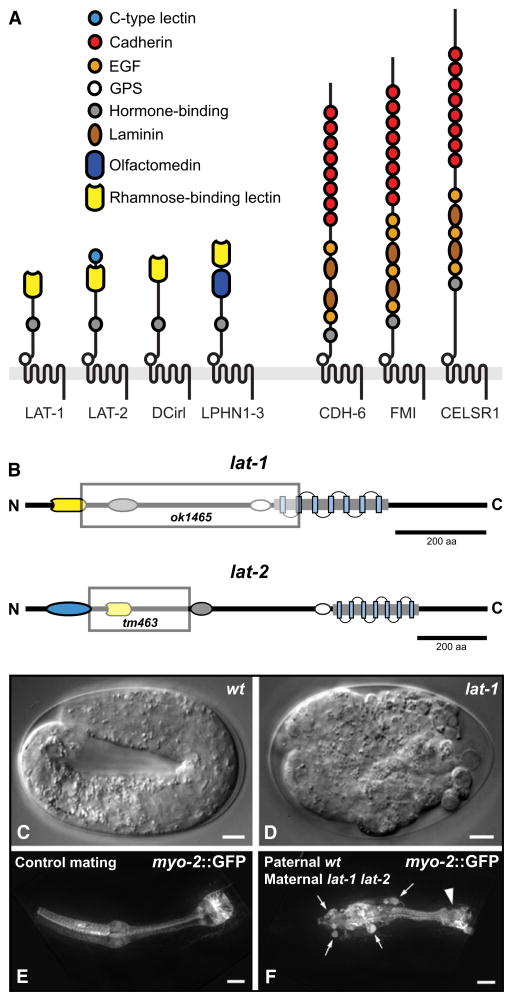
Figure 1. Evolutionary Conservation and Mutant Phenotype of lat-1.
(A) Domain architectures of LPHN and FMI proteins. C. elegans: LAT-1, LAT-2, CDH-6; Drosophila: DCirl, FMI; Homo sapiens: LPHN1–3, CELSR1–3.
(B) Mutant alleles used in this study. Shaded boxes represent the genomic deletions in lat-1(ok1465) and lat-2(tm463).
(C–F) Embryonic defects of latrophilin single mutants. (C) Elongated WT larva at pretzel stage. (D) A lat-1(ok1465) mutant lacking maternal and zygotic gene product. (E and F) Maternal effect of lat-1(ok1465). (C) Control larva heterozygous for myo-2p::gfp transgene. (D) Heterozygous offspring of homozygous lat-1 hermaphrodite. Ectopic pharyngeal cells (arrows) are labeled by paternally derived myo-2p::gfp and do not integrate into the pharynx; arrowhead: terminal bulb. Scale bars in (C) and (D) = 5 μm, in (E) and (F) = 10 μm.