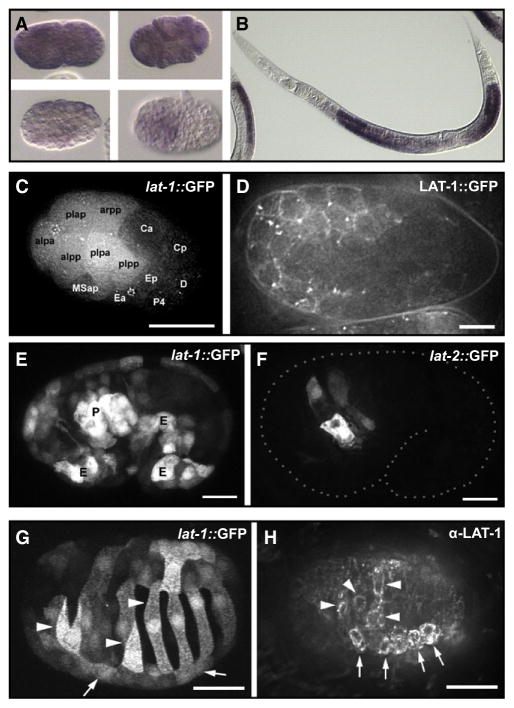
Figure 2. Expression Pattern of lat-1 and lat-2.
(A) lat-1 mRNA in early blastomeres and (B) the gonad detected by in situ hybridization. (C and D) Zygotic expression of lat-1 in early embryonic development.
(C) Expression of a lat-1p::gfp reporter gene at 26-cell stage. AB descendants are labeled “alaa” for ABalaa, etc.
(D) Membrane localization of a rescuing in-frame LAT-1::GFP fusion protein, 200-cell stage.
(E and F) Expression of lat-1 and lat-2 overlaps in the pharynx primordium. (E) lat-1p::gfp expression with strong signal in the pharyngeal primordium (“P”) and ventral epidermal precursors (“E”). (F) lat-2p::gfp expression at the same stage is confined to the pharynx primordium.
(G and H) Asymmetric expression of lat-1 in epidermal precursors during dorsal intercalation visualized with a lat-1p::gfp transgene (G) or by detection with an α-LAT-1 antibody. Arrows indicate position left seam cells, and arrowheads mark LAT-1-positive intercalating left dorsal epidermal cells. Scale bars in (C), (G), and (H) = 10 μm, in (D), (E), and (F) = 5 μm.