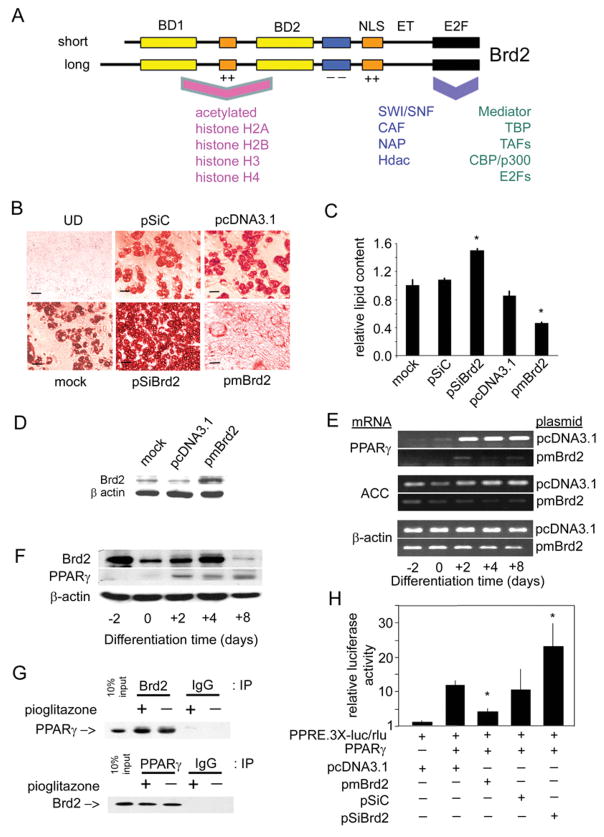
Figure 6. Brd2 inhibits adipogenic differentiation and co-represses PPAR-γ transcription.
(A) Schematic of Brd2 structure [4,14] and reported interacting proteins [18,19]. BD, bromodomain; NLS, nuclear localization signal; ET, extraterminal domain; E2F, E2F-complex association domain [19]; ++, basic domain; − −, acidic domain. Human and mouse Brd2 proteins are approx. 91 % identical. Associated proteins are discussed in the Introduction. CAF, chromatin assembly factor; NAP, nucleosome assembly protein. (B) Manipulation of Brd2 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes with Brd2 shRNA, Brd2 overexpression or controls. Oil Red O staining visualizes lipid content in cells that have undergone adipogenic differentiation. Adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes from pre-adipocytes was performed as described previously [58]. UD, undifferentiated (see the legend to Figure 4 for plasmid abbreviations). (C) Quantification of lipid content in transfected 3T3-L1 cells after adipogenic differentiation (n = 3; *P< 0.05). Lipid content using Oil Red O stain was determined as described previously [59]. (D) Immunoblot analysis verifies increased Brd2 expression in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes transfected with pmBrd2 or controls. (E) Overexpression of Brd2 with pmBrd2 suppresses normal expression of two adipogenic markers, PPAR-γ and ACC, as detected by RT–PCR at different time points during adipogenic differentiation. (F) Kinetics of Brd2 and PPAR-γ expression in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes during adipogenesis. (G) Co-immunoprecipitation (IP) of Brd2 and PPAR-γ in 3T3-L1 cells 3 days after induction of differentiation. IgG, non-specific control. (H) Brd2 inhibits PPAR-γ activity, as assessed by transcriptional activity of a PPAR-γ-driven luciferase reporter in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes, in response to manipulation of Brd2 (n = 3; *P< 0.05).