Figure 6. Expression of Lmo4 in the adult mouse brain.
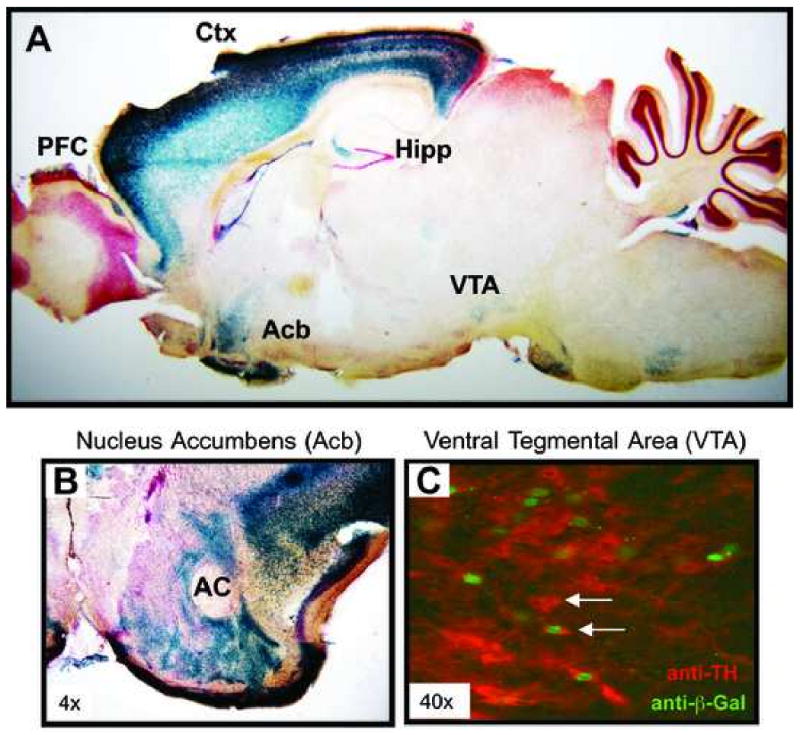
(A) Sagittal brain section of an adult Lmo4Gt/+ mouse stained with X-Gal (blue) to detect β-galactosidase expression (expressed as a Lmo4-β-galactosidase fusion protein). Intense β-galactosidase expression is observed in neocortex (Ctx; layers III and V), hippocampus (Hipp; CA3 regions and subiculum), and nucleus accumbens (Acb); low expression is also seen in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and some hypothalamic nuclei. Expression in baso-lateral amygdala and caudate putamen is not seen in this specific sagittal section. (B) Coronal section showing β-galactosidase expression in the Acb of a Lmo4Gt/+ adult mouse. (AC = anterior commissure). (C) Expression of LMO4-β-Galactosidase fusion protein in the VTA of a Lmo4Gt/+ mouse. Brain sections containing VTA were processed for β-galactosidase (green) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, red) antibody reactivity. Colocalization of LMO4 fusion protein and TH is observed in some (arrow), but not all (arrowhead) TH-positive dopaminergic neurons.
