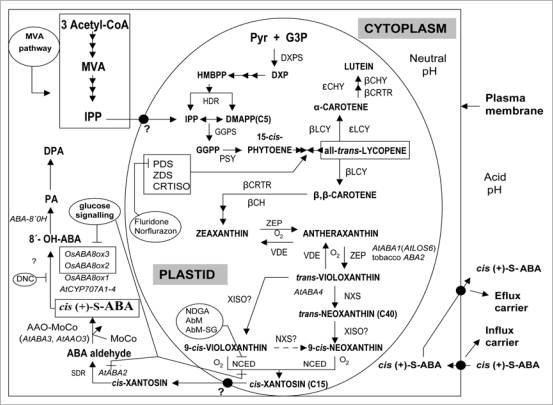
Figure 1.
ABA biosynthesis pathway, inhibitors and intracellular compartmentalization in higher plants. AbM, abamine; DMAPP, dimethylallyl di-P; DNC, diniconazole; DPA, dihydrophaseic acid; DXP, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-P; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-P; GGPP, geranylgeranyl di-P; HMBPP, hydroxymethylbutenyl 4-di-P; IPP, isopentenyl di-P; MVA, mevalonic acid; NDGA, nordihydroguaiaretic acid; PA, phaseic acid; Pyr, piruvate. Involved enzymes: AAO-MoCo, abscisic aldehyde oxidase or MoCo sulfurase; βCH, β-carotene hydroxylase; βCHY and βCRTR, β-ring hydroxylases; εCHY, ε-ring hydroxylase; ABA 8′-hydroxylase (Hordeum vulgare, HvABA8'OH); CRTISO, carotenoid isomerase; βCRTR, β-ring hydrolase; DXPS, DXP synthase; GGPS, geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase; HDR, HMBPP reductase; βLCY, lycopene β-cyclase; εLCY, lycopene ε-cyclase; NCED, 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxigenase (AtNCED1–9; maize, VP14; tomato, NOT); NXS, neoxanthin synthase; PDS, phytoene desaturase; PSY, phytoene synthase; SDR, member of short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases family; VDE, violoxanthin de-epoxidase; XISO, xanthophyll cis-isomerase (predicted); ZDS, ξ-carotene desaturase; ZEP, zeaxanthin epoxidase.