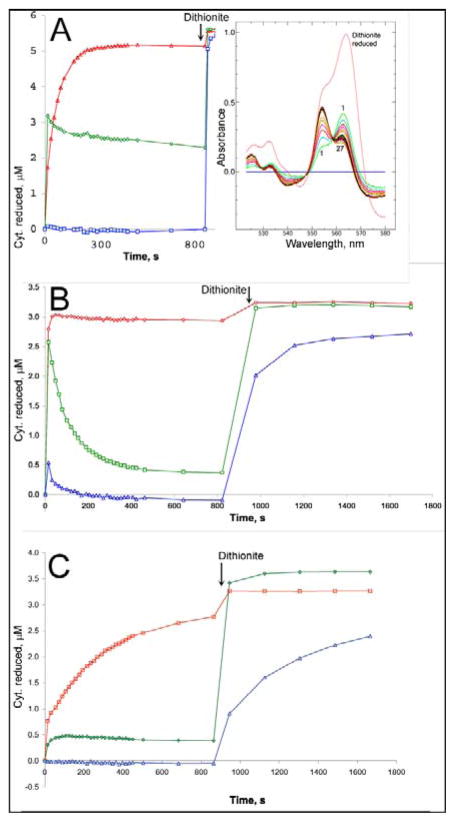
Figure 4. Ascochlorin inhibits reduction of cytochrome b in purified bovine cytochrome bc1 complex through either Qo or Qi site.
Bovine bc1 complex was diluted to ~6 μM (A) or 3 μM (B, C) in 20 mM potassium MOPS (pH 7.2), 100 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 5% glycerol, and 0.1 g/L dodecyl maltoside and supplemented with 14 μM azoxystrobin (A), 30 μM antimycin A (B), or 31 μM ascochlorin (C). A preliminary scan (scan 0) showed the complex to be fully oxidized. DBH2 was added to 25 μM and the sample was scanned repeatedly, at ~18 sec intervals initially, to follow the redox state of the cytochromes. After about 12 minutes, a trace of dithionite was added to the cuvette to determine the maximum extent of reduction. The initial oxidized spectrum was subtracted from all, and the resulting difference spectra (inset in A) were decomposed into sums of the difference spectra of cytochromes c1 (red), bH (green), and bL (blue) as described in “materials and methods” to determine the extent of reduction of each. The results are plotted against time.