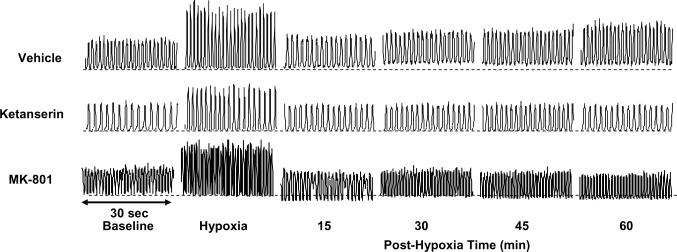
Fig. 1.
Representative tracings of the integrated glossopharyngeal nerve neurogram. These tracings were recorded before (baseline), during (hypoxia) and after acute intermittent hypoxia (AIH, 5 episodes of 3-min isocapnic 12% O2) in 3 rats, injected with vehicle (saline), ketanserin (2 mg/kg) and MK-801 (0.2 mg/kg), respectively. The horizontal dotted lines under the neurogram recordings represent the baseline magnitude of tonic integrated glossopharyngeal nerve activity. LTF exists in both phasic and tonic glossopharyngeal activity in the vehicle rat, but not in the ketanserin or MK-801 rat. There also appears to be tonic activity reduction in some post-hypoxia time points in the MK-801 rat, but this is not typical in the group data (see Fig. 5).