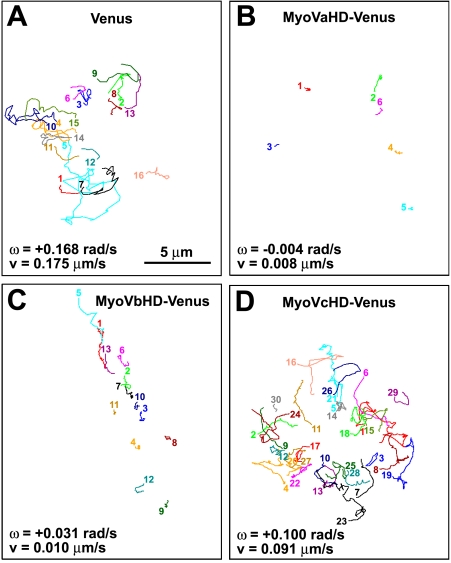
Figure 3.
The head domain of myosin Va or Vb inhibits the filopodial rotation. (A–D) The line sketches in each panel show trajectories of filopodial tips of a single growth cone that expresses Venus (A), MyoVaHD-Venus (B), MyoVbHD-Venus (C), or MyoVcHD-Venus (D). Each color corresponds to a single filopodium. All of the filopodial tips that appeared in the focal plane for a period of 5-min imaging were included in this study. The numbered end of each line represents the point where a filopodial tip first appeared in the focal plane, and the other end of the line is the point at which it moved out of the focal plane. The mean angular velocity (ω) and the mean velocity (v) of filopodial tips for each growth cone are shown. Positive and negative values of the angular velocity indicate right- and left-screw rotation, respectively.