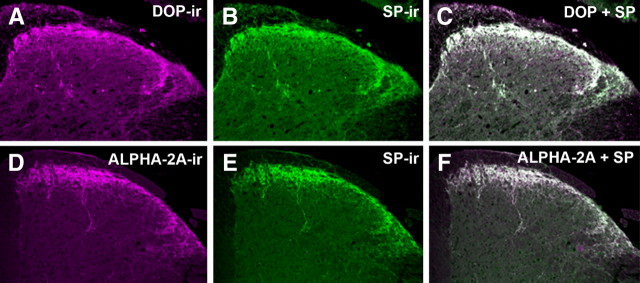
Figure 1.
Colocalization of α2AAR and DOP with SP in mouse spinal cord. A–C, Representative images of the dorsal horn of mouse spinal cord double-labeled with DOP (A, magenta) and SP (B, green) antisera. When images A and B are digitally merged (C), instances of colocalization appear as white. D–F, Representative images of mouse spinal cord double-labeled with α2AAR (D, magenta) and SP (E, Green) antisera. When images D and E are digitally merged (F), instances of colocalization appear white. The extensive colocalization observed between both α2AAR and DOP with SP suggests that α2AAR and DOP colocalize on SP-containing fibers in the mouse spinal cord. This extensive colocalization, already well characterized in rats (Riedl et al., 2009), appears to generalize to mice.