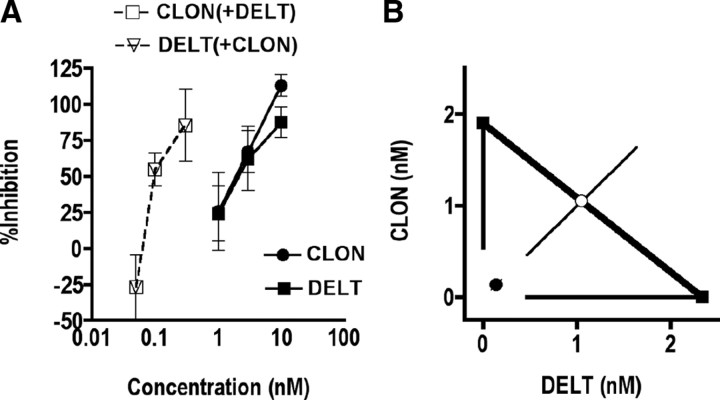
Figure 4.
Coadministration of DELT and CLON inhibits K+-evoked release of CGRP from spinal cord slices in a synergistic manner. A, K+-evoked release of CGRP was challenged by administration of DELT, CLON and their combination. DELT (filled squares) and CLON (filled circles) inhibited the release of CGRP in a concentration-dependent manner with similar potency and efficacy. Coadministration of DELT and CLON at constant concentration ratio of 1:1 (open squares and open triangles) was ∼30-fold more potent than either drug given alone, suggesting that the interaction was synergistic. Error bars represent mean ± SEM for each concentration point (n = 3–9 samples/concentration). B, Isobolographic analysis of the data in Figure 3A. The y-intercept represents the CLON EC50 (1.9 nm; 95% CI = 0.5–3.3), and the x-intercept represents the DELT EC50 (2.3 nm; 95% CI = 0.5–4.2) when each was administered alone. The heavy line connecting the intercepts is the theoretical additive line and the open circle represents the theoretical additive combined EC50. Coordinates for drug combinations falling below this line and outside the confidence limits indicate a synergistic interaction. Coadministration of CLON and DELT at a 1:1 concentration ratio resulted in an EC50 (0.06; 95% CI = 0.01–0.1) of DELT in the presence of CLON that fell well below the additive line, indicating that the interaction was synergistic. Error bars parallel to each axis represent the lower 95% CI for each compound given alone. The error bars on the combined concentration points represent the upper and lower 95% CIs.