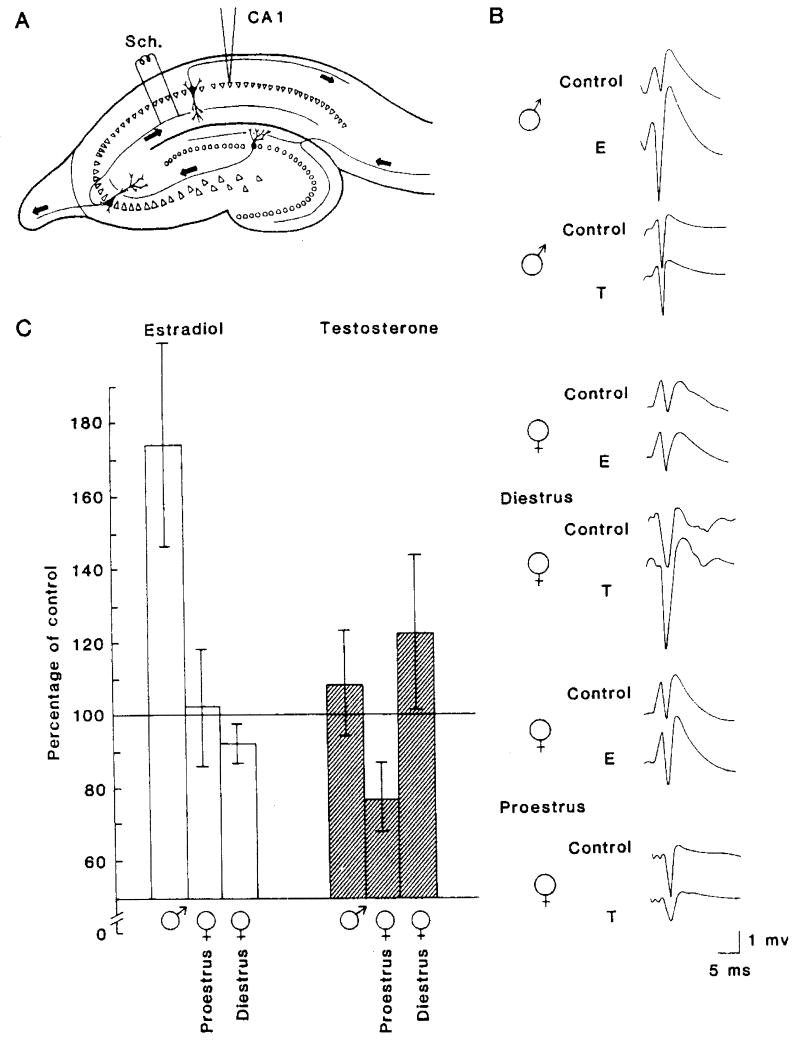
Figure 1.
(A) Diagram of a transverse hippocampal slice. Stimulating electrodes were located in the afferent pathway, which contains the Schaffer (Sch.) collaterals. Recording micropipettes were situated in the pyramidal cell body layer in CA1. Cells of this subfield receive monosynaptic input from the CA3 pyramids via the Schaffer collateral system.
(B) Representative field potentials from slice preparations in the various experimental conditions. Extracellular population spike responses to a given stimulus intensity are shown from the control period (before steroid administration) and after the administration of 1 × 10-10 M 17β-estradiol (E) or 1 × 10-10 M testosterone (T). Potentials from slices obtained from males and from proestrus and diestrus females are shown for purposes of comparison. All potentials are single sweeps recorded at the same voltage and time scales.
(C) Bar graph summarizing the major experimental outcomes. Values on the ordinate are mean percentages of spike amplitudes after steroid administration. Data for each condition are from 6 to 10 animals, each contributing one slice. Cursors representing magnitude of variability (standard error of the mean) are shown for each bar.
Reprinted with permission from [107]. Copyright 2008 American Association for the Advancement of Science.