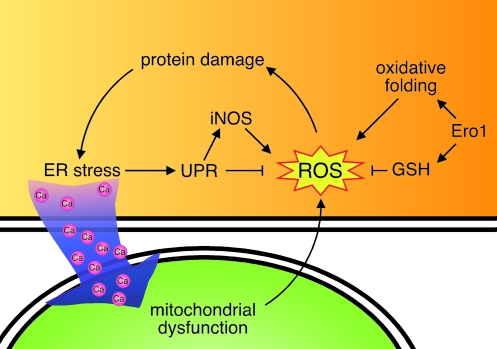
FIG. 7.
The UPR and ROS. Ero1-catalyzed oxidative folding leads to the production of ROS, which in turn can damage proteins in the ER and activate the UPR, leading to the production of proteins that detoxify ROS. Conversely, UPR activation causes calcium release from the ER, which leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and the production of more ROS. Ero1 also leads to increases in GSH, which suppresses ROS, demonstrating the opposing functions of Ero1 and the UPR in regulating ROS. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).