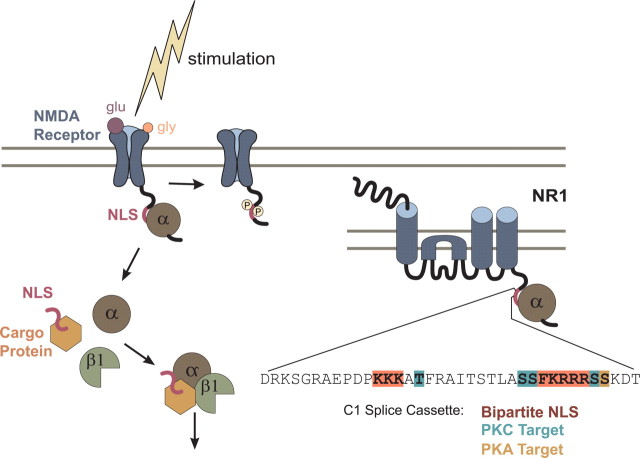
Figure 6.
In our model, importin α binds the NLS in the cytoplasmic tail of NR1. Upon stimulation, importin α is released from the NMDA receptor, binds synaptically localized soluble NLS-containing cargoes, and together with importin β1, transports them to the nucleus. Synaptic stimulation activates PKC, which phosphorylates residues flanking the NLS in NR1-1a, thereby disrupting importin α binding. Enlargement of the NR1 subunit shows the amino acid sequence of exon 21/cassette C1 containing the NLS (orange), and residues flanking the NLS that are PKC (blue)/PKA (brown) targets of phosphorylation.