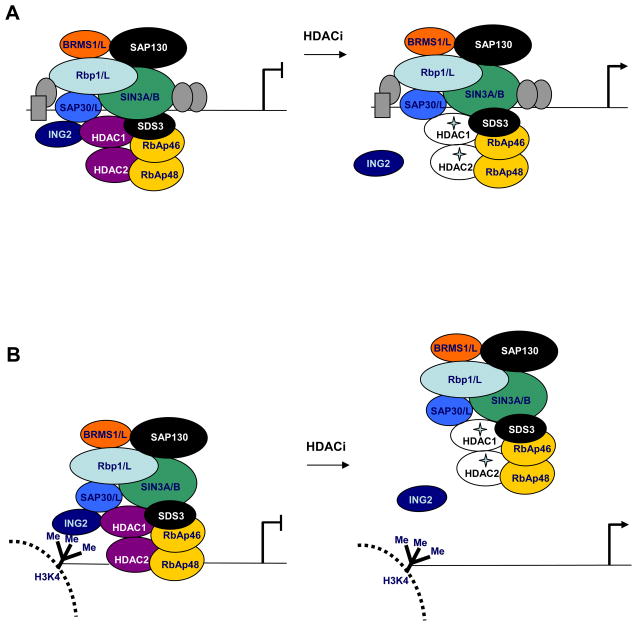
Figure 5. Models for gene activation after HDAC inhibitor treatment.
a. The Sin3 complex can be tethered to chromatin through interactions of Rbp1 or Sin3 subunits with transcription factors (gray ovals and rectangle) and through SAP30/SAP30-LIKE and RbAp46/48 subunits. At these promoters, HDAC inhibitors cause inactivation of the HDACs and dissociation of ING2 from the complex. b. ING2 is required for tethering the Sin3 complex at some promoters where H3K4 is di/tri-methylated. At these regions, HDAC inhibitor treatment causes inactivation of the HDACs as well as dissociation of the Sin3 complex from chromatin.