Figure 1.
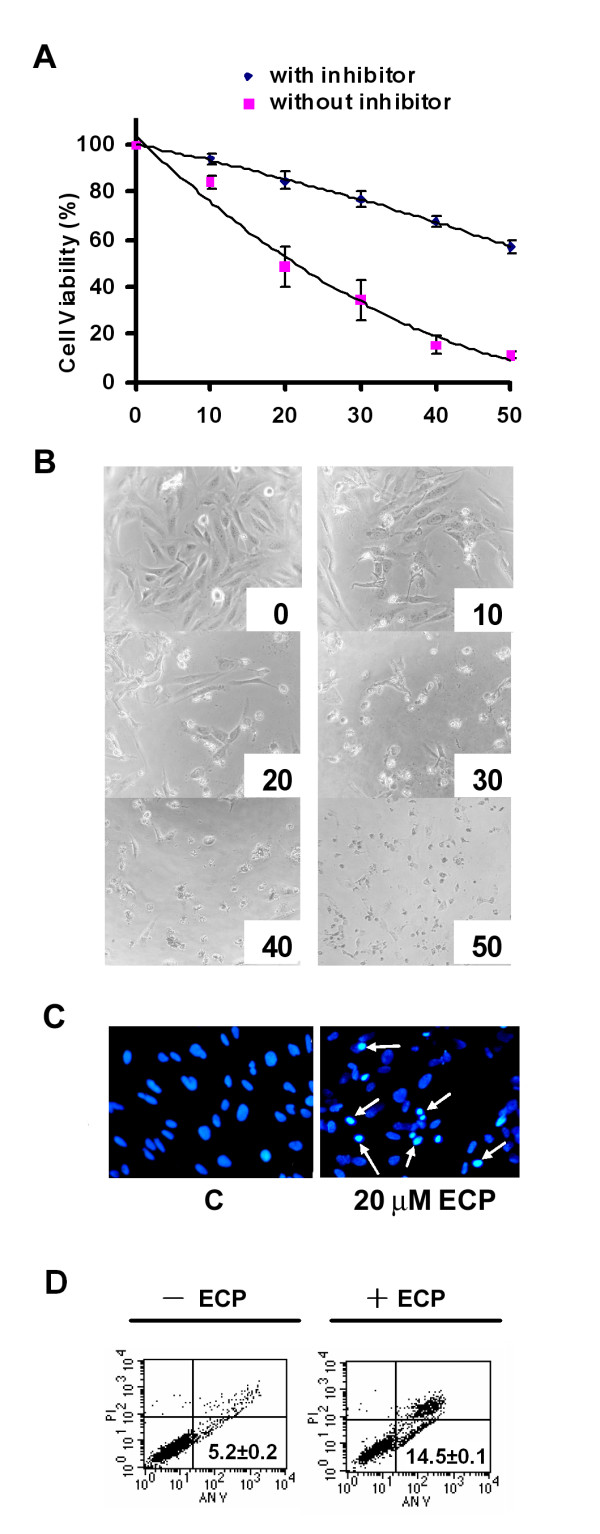
Effect of rECP on the viability of BEAS-2B cells. BEAS-2B cells (5 × 103) were incubated in a 96-well plate and treated with various concentrations of rECP as indicated for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. (A) Cells were treated with rECP (up to 50 μM) for 48 h in the presence or absence of the general caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK. (B) Morphology of the cells treated with serial concentrations of rECP ranging from 0 to 50 μM (concentrations shown below each panel). (C) Nuclei of BEAS-2B cells were stained with Hoechst 33342. Cells were treated or untreated with 20 μM rECP for 48 h. Stained nuclei were visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The chromatin condensation is indicated by bright blue spots shown by white arrows. (D) BEAS-2B cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 20 μM rECP for 24 h. The cells were stained with annexin-V-FITC and analyzed by FACS. Intact cells are located in the lower left quadrant. The apoptotic cells stained by annexin-V-FITC are located in the lower right quadrants, respectively. All data represent the arithmetic mean ± SEM.
