Figure 2.
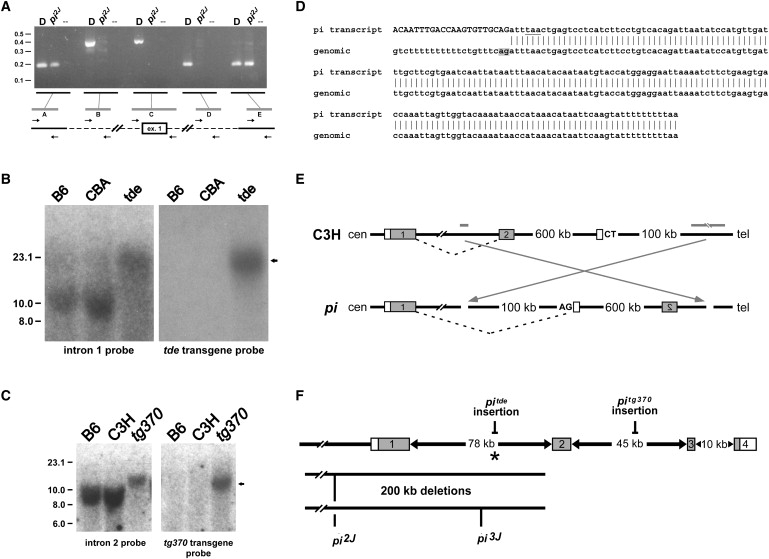
Genomic Alterations within Grxcr1 Are Present in Each of the Pirouette Alleles
(A) PCR products were amplified from genomic DNA of control DBA/2J (“D”) and homozygous pi2J mice, with the use of primer pairs (“A”–“E”) designed from sequences upstream of exon 1, immediately flanking exon 1, and within intron 1. The distance between pairs A and E in normal genomic DNA is approximately 200 kb and represents the maximum size of a deletion in the mutant. The distance between pairs B and D is approximately 175 kb and represents the minimal size of the deletion. The deletion breakpoint in intron 1 is located within the 9 kb region between pairs D (no amplification in pi2J DNA) and E (positive for amplification in both control and pi2J DNA), approximately 3 kb upstream of exon 2. Positions of molecular-size standards are indicated at left in kilobases.
(B) Southern blots containing EcoRV-digested genomic DNA from control (C57BL/6J, B6; CBA/CaJ, CBA) and homozygous pitde mice were hybridized with a probe derived from genomic sequences 32 kb upstream of exon 2 (left panel), stripped, and rehybridized with a probe complementary to the tde transgene construct (right panel). The arrow indicates common-sized 20 kb fragments that hybridize with both probes only in pitde DNA, consistent with insertion of the tde transgene into this region of intron 1.
(C) Southern blots containing EcoRI-digested genomic DNA from control (C57BL/6J, B6; C3He/FeJ, C3H) and homozygous pitg370 mice were hybridized with a probe derived from genomic sequences 25 kb downstream of exon 2 (left panel), stripped, and rehybridized with a probe complementary to the tg370 transgene construct (right panel). The arrow indicates common-sized 13 kb fragments that hybridize with both probes only in pitg370 DNA, consistent with insertion of the tg370 transgene into this region of intron 2.
(D) The sequence of a hybrid Grxcr1 cochlear transcript detected in affected pi mice. The top sequence is from a 3′ RACE product amplified with the use of nested primers derived from exon 1 of Grxcr1. The upper-case nucleotides indicate identity to the 3′ end of exon 1. The underlined nucleotides indicate a stop codon that would result in a truncated GRXCR1 protein. Vertical bars represent identity to genomic sequence located 600 kb telomeric of Grxcr1 (bottom, in telomere-to-centromere orientation). The gray box denotes a cryptic splice acceptor signal; an adjacent polypyrimidine tract is also present.
(E) Structure of a predicted chromosomal inversion in pi. Gray bars represent the relative position in the WT background strain C3H of putative inversion breakpoints located in intron 1 of Grxcr1 and in a region approximately 700 kb telomeric (see Figure S3). Gray boxes indicate the first two exons of Grxcr1. The open boxes represent the cryptic exon detected by 3′ RACE. An inversion in the pi allele (arrows) would place the cryptic exon in the correct orientation for inclusion in the hybrid transcript with exon 1 of Grxcr1, with the use of the AG splice acceptor signal shown.
(F) Summary of the Grxcr1 mutations in each of the pirouette alleles. The asterisk indicates the position of the putative centromeric inversion breakpoint in the original pi allele.
