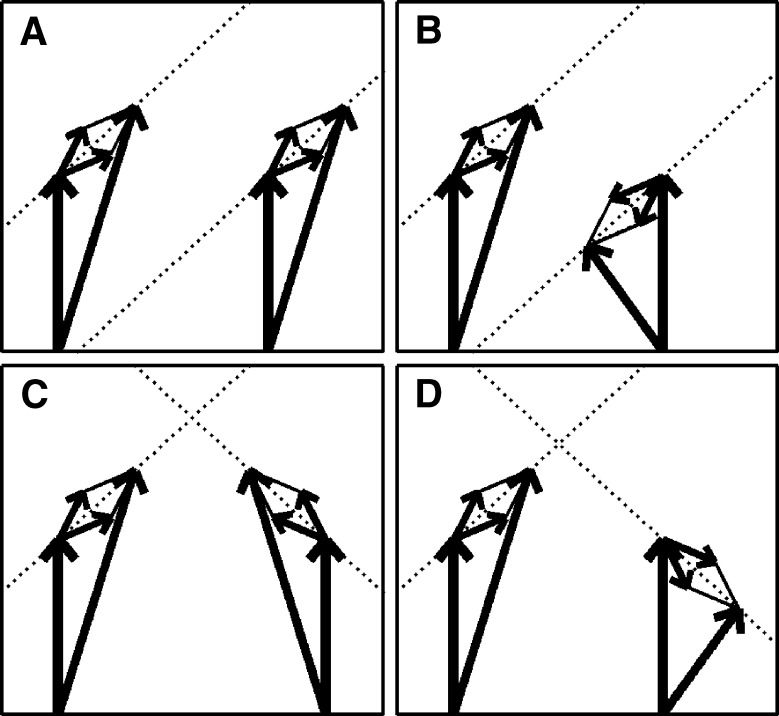
FIG. 3.
Binaural modulation. Each panel shows a pair of vector diagrams representing the stimuli presented to the two ears. The stimulus to each ear contains a mixed modulation as in Figure 2. Different choices of interaural phases of the sidebands lead to different binaural modulations. A Diotic modulation: modulations are interaurally identical; B mixed binaural modulation: both phase and amplitude modulation are interaurally phase-reversed; C binaural QFM: phase modulation is interaurally phase-reversed, while amplitude modulation is diotic; D binaural AM: amplitude modulation is phase-reversed, while phase modulation is interaurally in phase (though not completely identical).