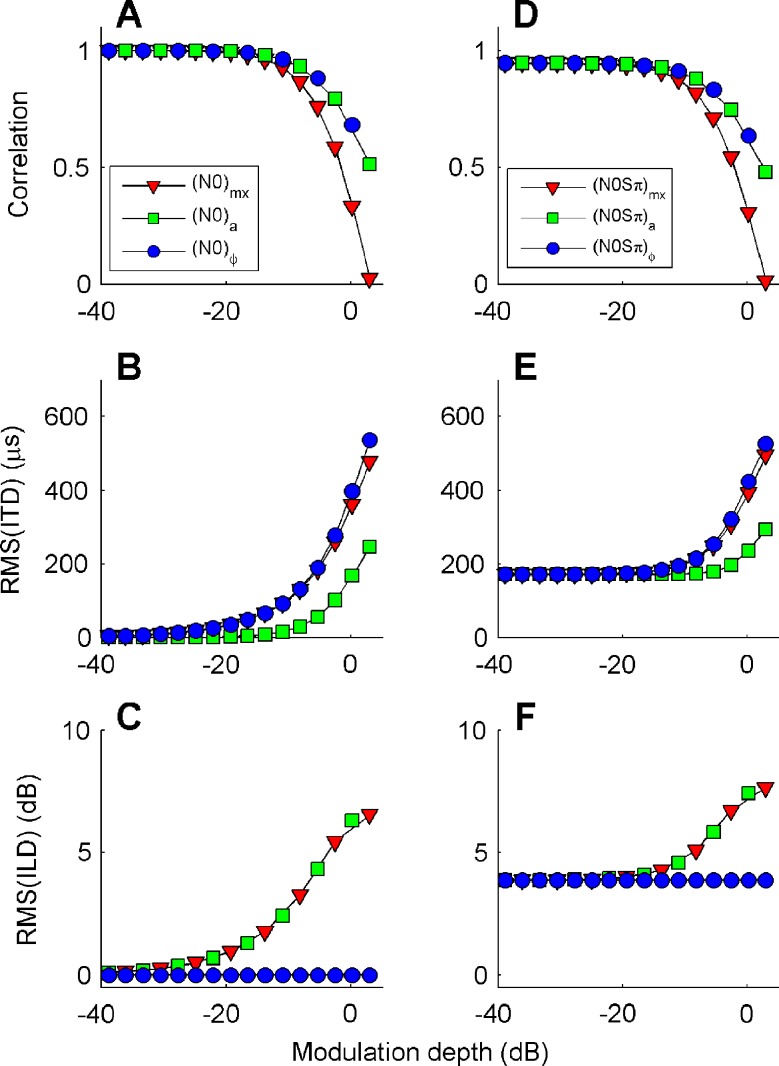
FIG. 4.
The effect of depth of binaural modulation on three metrics of binaural disparity: normalized interaural correlation (A, D); RMS of dynamic ITD (B, E) and ILD (C, F). Symbols indicate the type of binaural modulation imposed on the stimulus: mixed (mx triangles), binaural AM (a squares), and binaural QFM (ϕ circles). In the left column (A, B, and C), the binaural modulation was applied to a diotic noise stimulus. In the right column (D, E, and F), the binaural modulation was applied to the sum of a diotic noise and an Sπ tone at –15 dB S/N ratio. In all cases, the binaural metrics were evaluated on a 100-Hz-wide noise band centered at 500 Hz.