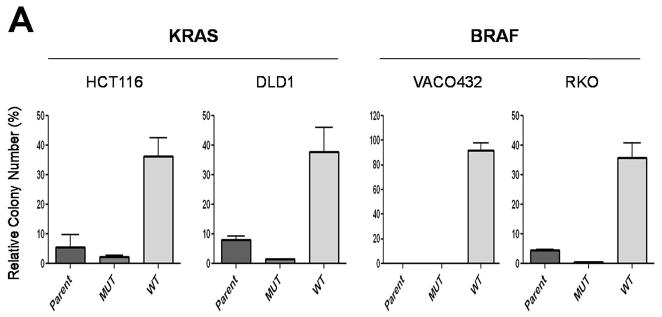
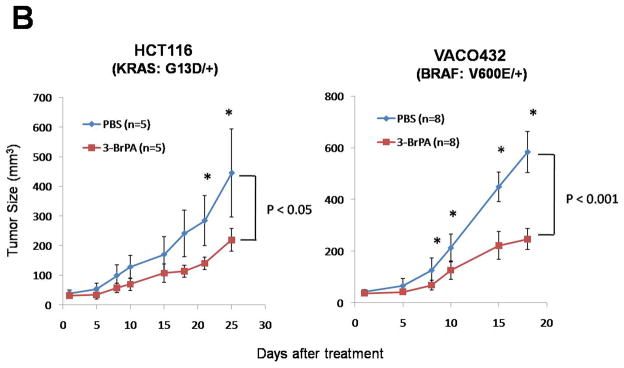
Fig. 4.
The glycolysis inhibitor 3-BrPA is selectively toxic to cells with mutant KRAS or BRAF alleles. (A) Colony formation was assessed after 3-BrPA treatment (110 μM) for three days. Colony counts were normalized to those obtained from cells subjected to the same procedure without exposure to 3-BrPA. The differences between MUT and WT clones were statistically significant in all cases (P < 0.008, Student’s t-test). (B) Mice with subcutaneous tumors established from HCT116 (KRAS: G13D/+) or VACO432 (BRAF: V600E/+) cells were injected intraperitoneally with 3-BrPA or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) daily for two weeks. “n” represents the number of mice used in each group. Points and error bars represent the means and SD for each group of mice. Asterisks denote times when there were significant differences between the tumor sizes in the PBS vs. 3-BrPA groups (P < 0.05, Student’s t-test).