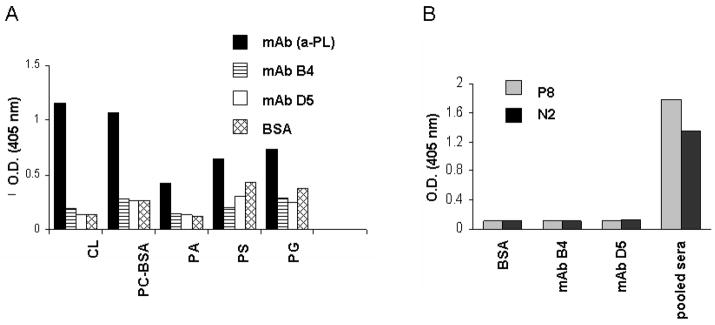
Figure 4.
Monoclonal Ab B4 does not cross-react with previously published antigens recognized by pathogenic natural Abs in intestinal IR injury. A, Monoclonal Ab B4 was tested in an anti-phospholipid Ab ELISA for the binding to cardiolipin (CL), phosphorylcholine-BSA (PC-BSA), phosphatidic acid (PA), phosphatidylserine (PS), and phosphatidylglycerol (PG). A broadly reactive IgM anti-phospholipid mAb (our unpublished data) was used as a positive control. Bound Abs were detected by AP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgM. Data are shown as OD405nm. B, Bar graph shows the lack of reactivity of mAb B4 in ELISA with synthetic peptides reported to be targets for the pathogenic CM22 IgM mAb. Synthetic peptides coated to an ELISA plate were incubated with either mAb B4 or control mAb D5. Bound antibodies were detected by AP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgM Ab. Pooled sera from C57BL/6 mice at a dilution of 1/50 were used as a positive control. Data are shown as OD405nm and are representative of two independent experiments.