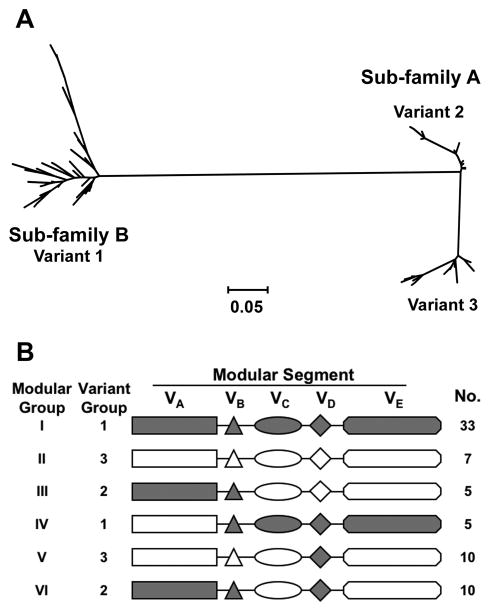
Figure 5.
A. Phylogram of 70 unique fHbp amino acid sequences showing division of the proteins into 2 subfamilies, designated as A and B by Fletcher et al. [100]. Subfamily B contains the proteins in the variant 1 group described by Masignani et a. [61]. Subfamily A is subdivided into 2 branches, designated by Masignani et al. as variants 2 and 3, respectively. Each branch represents a distinctive protein sequence. The scale bar represents 5 amino acid differences per 100 amino acids. B. Modular structure. The architecture of fHbp consists of different combinations of five variable segments, designated VA to VD [116]. Each segment is derived from one of two genetic lineages, designated alpha (gray segments) or beta (white segments). All of the distinctive fHbp protein amino acid sequences referred to in Panel A could be assigned to one of six “modular groups”, designated I–VI. Panel B is reprinted from Microbiology 2009;155:2873–83. Copyright ©2009 by the Society for General Microbiology.