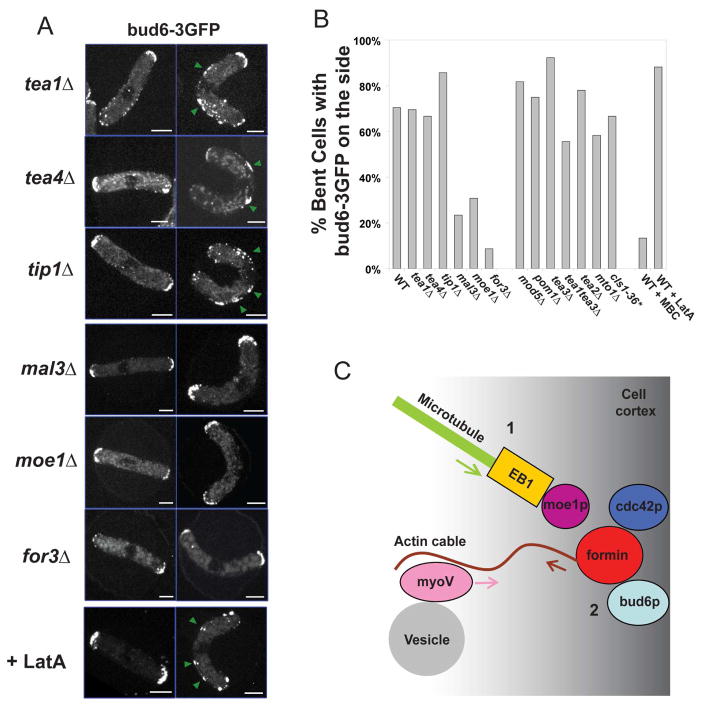
Figure 6. Recruitment of polarity factors by MTs is independent of the tea1-tea4p pathway, but requires mal3p, moe1p, for3p and the secretory pathway.
(A) Bud6-3GFP position in normal and bent cell of the indicated mutants, and in cells treated with the indicated chemicals. Strains: NM14, NM34, NM30, NM48, NM117, NM115, NM01 (all cdc25-22 at 25°C). Scale bars: 5μm. (B) Proportion of bent cells that show a specific location of bud6-3GFP to the cell side in the indicated genetic backgrounds and conditions (n≈30 for each condition). Some mutants and the corresponding strain numbers are shown in Figure S9. *For this experiment, the temperature of the objective was raised to 30°C with a Bioptechs objective heater. (C) Proposed model for how MT contact induces sites of cell polarization at the cortex: 1. A MT plus end contacts the cortex and recruits for3p (formin) bud6p and cdc42p. This recruitment is dependent on mal3p (EB1) and moe1 (EB1-binding protein). 2. The formin assembles actin cable structures from these sites. 3. Actin filaments guide the transport of myosin V and its cargo such as vesicles towards these ectopic sites.