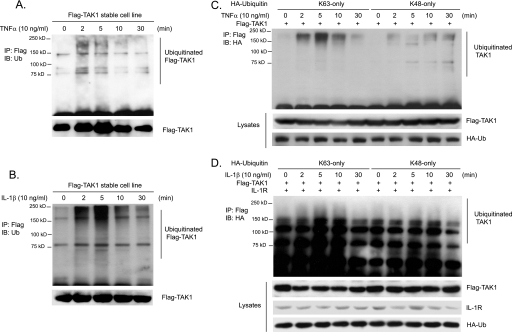
FIGURE 1.
TNFα and IL-1β induce Lys63-linked TAK1 polyubiquitination. A and B, TNFα and IL-1β induce TAK1 polyubiquitination. HeLa cells with stable expression of FLAG-TAK1 were either untreated or treated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) (A) and IL-1β (10 ng/ml) (B) for the times indicated and subsequently lysed. FLAG-TAK1 proteins in the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibodies and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-ubiquitin antibodies to detect the presence of ubiquitinated FLAG-TAK1. C, TNFα induces Lys63-linked TAK1 polyubiquitination. Expression vectors encoding FLAG-TAK1 were co-transfected into HEK-293T cells with expression vectors encoding HA-ubiquitin-Lys63 only and Lys48 only, respectively. Then cells were either untreated or treated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for the time points indicated and subsequently lysed. FLAG-TAK1 proteins in the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies and immunoblotted with anti-HA antibodies to detect the presence of ubiquitinated FLAG-TAK1. D, IL-1β induces Lys63-linked TAK1 polyubiquitination. Expression vectors encoding FLAG-TAK1 and IL-1R were co-transfected into HEK-293T cells with expression vectors encoding HA-ubiquitin-Lys63-only and Lys48-only, respectively. Then cells were either untreated or treated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for the times indicated and subsequently lysed. FLAG-TAK1 proteins in the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies and immunoblotted with anti-HA antibodies to detect the presence of ubiquitinated FLAG-TAK1.