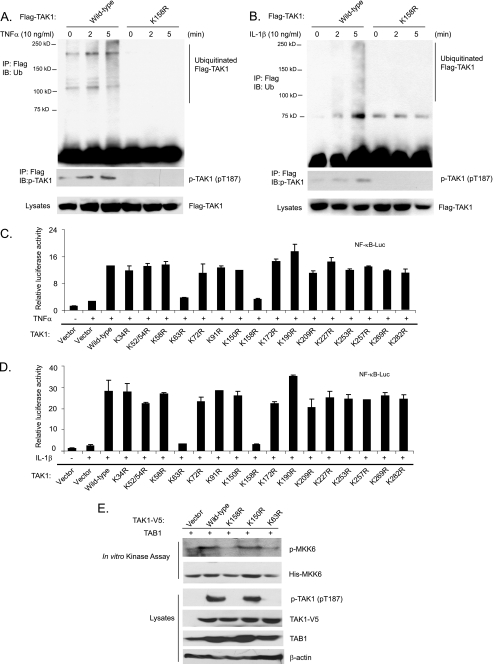
FIGURE 4.
TNFα and IL-1β induce TAK1 polyubiquitination at the Lys158 residue. A and B, TNFα and IL-1β induce TAK1 polyubiquitination at Lys158. HeLa cells with stable expression of FLAG-TAK1 wild type and K158R mutant were either untreated or treated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) (A) and IL-1β (10 ng/ml) (B) for the time points indicated and subsequently lysed. FLAG-TAK1 proteins in the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibodies and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-ubiquitin antibodies to detect the presence of ubiquitinated FLAG-TAK1. C and D, the effect of overexpression of TAK1 lysine to arginine mutants on TNFα-induced (C) and IL-1β-induced (D) NF-κB activation. NF-κB luciferase reporter and control Renilla luciferase reporter vectors were co-transfected into TAK1-deficient MEF cells with empty vector or expression vectors encoding TAK1 wild type and lysine to arginine mutants for 48 h, respectively. Cells were then either untreated or treated with TNFα (1 ng/ml) and IL-1β (1 ng/ml) for 6 h. The relative luciferase activity was measured and normalized with the Renilla activity. The error bars indicate ±S.D. in triplicate experiments. E, TAK1 Lys158 is required for TAK1 activation. TAB1 were transfected into HEK-293T cells with TAK1-V5 wild type, K158R, K150R, and K63R, respectively. TAK1-V5 proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts with anti-V5 antibodies for an in vitro kinase assay using recombinant His-MKK6 as a substrate.