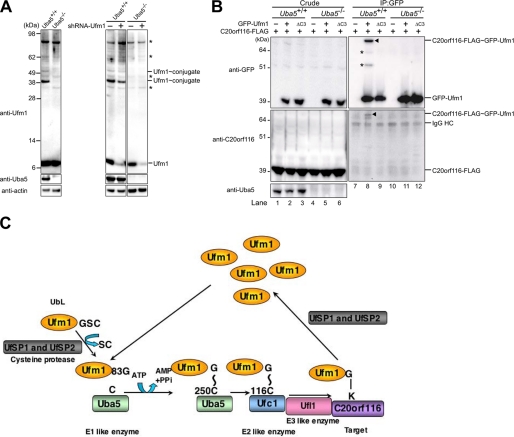
FIGURE 6.
Impairment of Ufm1 conjugation in Uba5 knock-out mice. A, Ufm1 conjugation in Uba5 knock-out MEFs. MEFs prepared from embryonic day 10.5 Uba5+/+ and Uba5−/− were lysed, and the lysates were analyzed by immunoblot with anti-Ufm1, anti-Uba5, and anti-actin antibodies. A knockdown of Ufm1 was not accompanied by any change of the ∼35-, ∼40-, ∼62-, and ∼90-kDa Ufm1-reactive proteins, whereas levels of free Ufm1 and the 39- and 51-kDa proteins (the latter two proteins were not recognized in Uba5 knock-out MEFs) were decreased by the knockdown (right-hand panels). Thus, we concluded that the ∼35, ∼40, ∼62, and ∼90 kDa bands indicated by asterisks are nonspecific. B, Uba5 is indispensable for C20orf116 conjugation with Ufm1. Uba5+/+ (lanes 1–3) and Uba5−/− (lanes 4–6) MEFs were stably transfected with C20orf116-FLAG (lanes 1–6) together with GFP-Ufm1 (lanes 2 and 5) or GFP-Ufm1ΔC3 (lanes 3 and 6), and then the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody (lanes 7–12). The lysates (Crude) and immunoprecipitants (IP) were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. The bands corresponding to GFP-Ufm1, C20orf116-FLAG, C20orf116-FLAG·GFP-Ufm1, and IgG HC are indicated. *, unknown proteins conjugated with GFP-Ufm1. The data shown in A and B are representative of three experiments with similar results. C, overall features of the Ufm1 conjugation pathway. G∼C, thioester linkage; G-K, isopeptide bond.