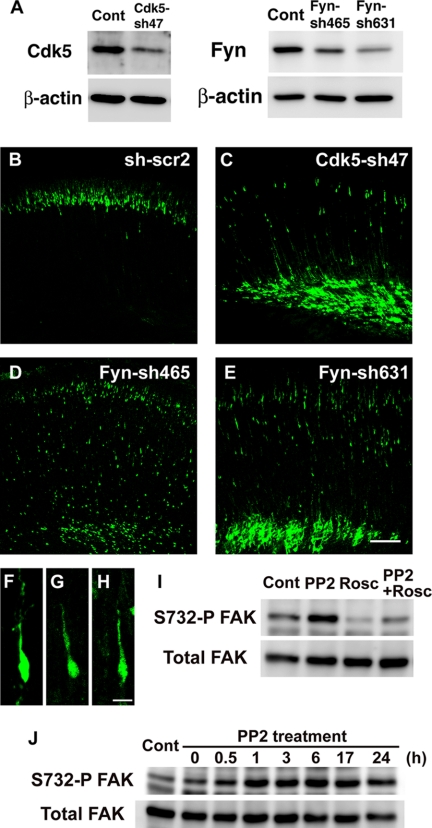
FIGURE 7.
Knockdown of Cdk5 and Fyn caused defects in neuronal migration. A, amount of Cdk5 and Fyn proteins in primary cortical neurons transfected with the indicated shRNA vectors. Primary cortical neurons from E15 cerebral cortices were transfected with the indicated plasmids and incubated for 2 days in vitro. The cell lysates were subjected to the immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies to evaluate the efficiency for RNAi. B–E, embryonic brains electroporated with control scrambled shRNA (sh-scr2) (B), Cdk5-sh47 (C), Fyn-sh465 (D), or Fyn-sh631 (E) plus EGFP-expressing vectors at E14, followed by fixation at P0. F–H, Cdk5 or Fyn-knockdown cells in the cortical plate exhibited locomoting morphology with a leading process. F, Cdk5-sh47; G, Fyn-sh465; H, Fyn-sh631; and I and J, primary cortical neurons from E15 cerebral cortices were treated with PP2 for 3 h (I) or the indicated time (J), and subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Control (Cont) is cell lysates treated with DMSO for 3 h (I) or 6 h (J). Because Ser-732 phosphorylation on FAK is known to be a good and specific substrate of Cdk5, we used the FAK phosphorylation as an indicator for Cdk5 activity. Scale bars, 100 μm (B–E) and 10 μm (F–H).