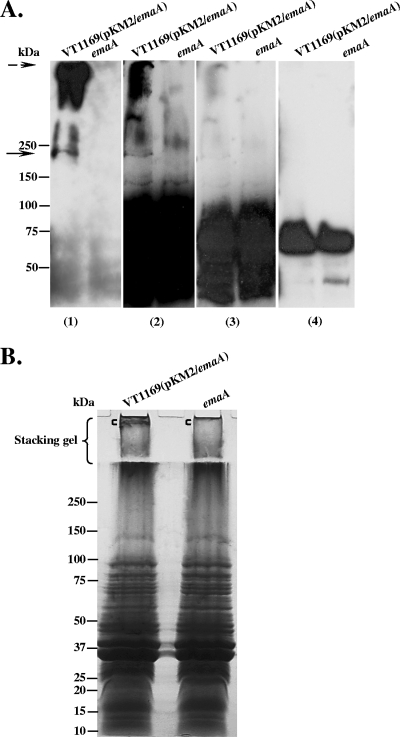
FIG. 5.
Fucose-specific Lens culinaris agglutinin (LCA) blots of membrane proteins from EmaA-producing and emaA mutant strains. Equivalent amounts of membrane proteins from the EmaA-overproducing strain VT1169 (pKM2/emaA) and the emaA mutant (emaA) were prepared, loaded into the 4 to 15% polyacrylamide Tris-HCl gel, and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. (A) The same protein-transferred membrane was probed with anti-EmaA monoclonal antibody (panel 1); biotinylated LCA, with different exposure times of the film (panels 2 and 3); and avidin alone (nonlectin control) (panel 4). Antibody binding was detected using goat anti-mouse antibodies, and lectin binding was detected using avidin. The solid arrow at ∼200 kDa corresponds to the EmaA monomer. The dashed arrow corresponds to EmaA aggregates associated with the stacking gel. (B) Colloidal blue stain of membrane proteins. Equivalent amounts of membrane proteins from the EmaA-overproducing strain VT1169(pKM2/emaA) and the emaA mutant strain were separated in a 5 to 15% polyacrylamide-SDS gel with a 3% stacking gel. Following electrophoresis, the gel was stained with colloidal blue. The region of the gel corresponding to the EmaA aggregates, shown with the square bracket ([) in the stacking gel, and a similar region of the gel in the emaA mutant ([) were excised and analyzed using LC/MS (Table 4).