Figure 5.
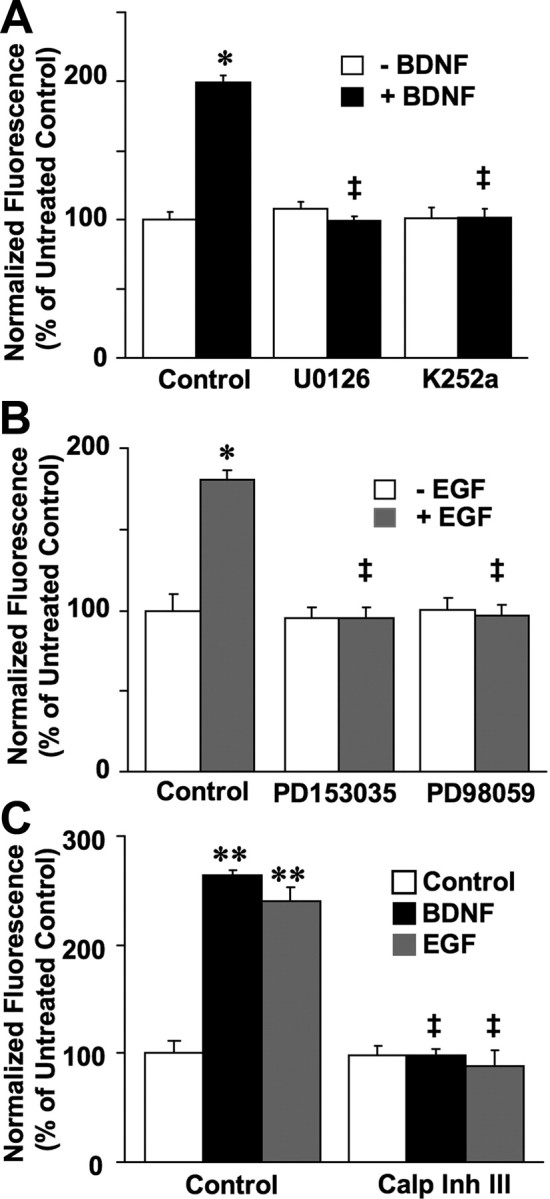
Calpain activation induced by BDNF and EGF in cortical neurons depends on MAPK. A, BDNF-elicited calpain activation in cortical neurons is blocked by inhibitors of MAP kinase and TrkB receptor. Fluorescence was measured 20 min after BDNF (50 ng/ml) addition to cortical neurons preloaded with the FRET substrate and pretreated with U0126 (10 μm) or K252a (0.5 μm). Results are expressed as normalized fluorescence (percentage of untreated control values) and are means ± SEM of five experiments with a total of 6–14 readings per condition. *p < 0.05 compared with control; ‡p < 0.01 compared with BDNF control samples. B, EGF-elicited calpain activation in cortical neurons is inhibited by MAP kinase inhibition or ErbB1receptor inhibition. Fluorescence was measured 20 min after EGF (20 ng/ml) addition to cortical neurons preloaded with the FRET substrate and pretreated with PD98059 (25 μm) or PD153035 (0.5 μm). Results are expressed as normalized fluorescence (percentage of untreated control values) and are means ± SEM of six experiments. *p < 0.05 compared with control; ‡p < 0.01 compared with EGF control samples. C, BDNF- and EGF-induced calpain activation in cortical neurons is blocked by calpain inhibitor III. Fluorescence was measured 20 min after BDNF (50 ng/ml) or EGF (20 ng/ml) addition to cortical neurons preloaded with the FRET substrate and pretreated with calpain inhibitor III (10 μm). Results are expressed as normalized fluorescence (percentage of untreated control values) and are means ± SEM of six to eight experiments. **p < 0.01 compared with control; ‡p < 0.01 compared with BDNF or EGF control samples.
