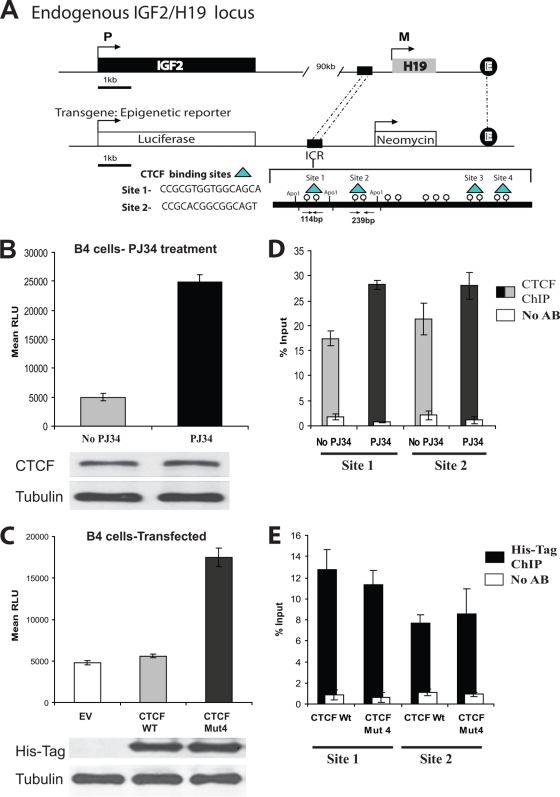
FIG. 4.
CTCF insulator function at the H19 ICR in a transgenic model is dependent on PARylation. (A) In vitro epigenetic reporter system: a schematic diagram of the stably integrated luciferase reporter construct in the 293T transgenic cell line B4. The integrated construct contains a luciferase gene under the control of the mouse Igf2 promoter (P3), an H19 enhancer, and the upstream H19 ICR. The ICR contains four identified binding sites for the CTCF protein (indicated). (B) The activity of the luciferase gene controlled by the Igf2 promoter is increased in the presence of the PARP inhibitor PJ34. B4 cells (6 × 105) were plated and either treated or not treated with 10 μM PJ34. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were counted and lysed and the luciferase assay was performed. The luciferase values were normalized based upon cell number. Bars represent luciferase activity in relative luciferase units (RLU). Each bar shows an average of results from three experiments performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviations. The levels of CTCF in the cell lysates were assessed by Western blotting using the anti-CTCF antibody. The membrane was reprobed with an antitubulin antibody as an internal control for cell number (results are shown at the bottom). (C) The activity of the luciferase gene controlled by the Igf2 promoter is increased in cells transfected with the vector expressing CTCF Mut4, which is deficient in PARylation. B4 cells (4 × 105) were transfected with 5 μg of either the EV or a vector expressing the CTCF WT or CTCF Mut 4 and 0.5 μg of the β-galactosidase-expressing construct. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, the cells were counted, lysed, and subjected to the luciferase assay. The luciferase values were initially normalized by cell number, and the transfection efficiency was then normalized using the β-galactosidase assay. Bars represent luciferase activity in relative luciferase units. Each bar shows an average of results from three experiments performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviations. The levels of exogenous CTCF were assessed by Western blotting using the anti-His tag antibody. The membrane was reprobed with an antitubulin antibody as an internal control for cell number (results are shown at the bottom). (D) Endogenous CTCF is associated with the CTCF binding sites 1 and 2 at the H19 ICR in B4 cells not treated and treated with PJ34. B4 cells (5 × 106) were either treated or not treated with 10 μM PJ34 for 24 h, cells were cross-linked with formaldehyde, and the standard ChIP assay was performed to assess the in vivo CTCF occupancies at the DNA. To separate two CTCF binding sites, site 1 and site 2, the DNA-protein complexes were digested overnight with ApoI restriction endonuclease and subjected to IP with the anti-CTCF antibody. Real-time PCR amplification was carried out using primers situated within site 1 and site 2. The efficiency of ChIP at each of the sites was calculated as a percentage of the starting material (percent input). Results are a representative example of data from three independent experiments. (E) Exogenous CTCF is associated with the CTCF binding sites 1 and 2 at the H19 ICR in B4 cells transfected with the plasmids expressing the CTCF WT and CTCF Mut4. B4 cells (5 × 106) were transfected with a plasmid expressing either the His-tagged CTCF WT or CTCF Mut4. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, the cells were cross-linked with formaldehyde and the standard ChIP assay was performed to assess the in vivo occupancies at the DNA. To separate two CTCF binding sites, site 1 and site 2, the DNA-protein complexes were digested overnight with ApoI restriction endonuclease and subjected to IP with the anti-His tag antibody. Real-time PCR amplification was carried out using primers situated within site 1 and site 2. The efficiency of ChIP at each of the sites was calculated as a percentage of the starting material (percent input). Results are a representative example of data from three independent experiments.