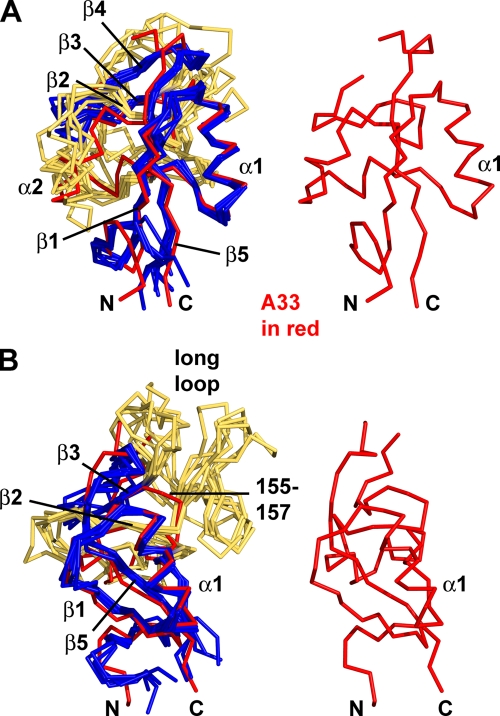
FIG. 2.
Overlays of A33 and five other CTLD structures in stick representations. (A) A33 (red) is overlaid with five other CTLDs (blue and yellow, at left) and is shown alone (at right and in panel B) to orient the reader. The other CTLDs are colored blue where they exhibit the more conserved portions of a C-type lectin-like fold and are colored yellow where they are not as conserved. Conserved secondary structure elements are labeled from N to C termini: β1, α1, α2, β2, β3, β4, and β5. Note that A33 does not contain a β4 strand. The β2 strand of A33 (red) and the β2 strands of the other CTLDs (“β2,” colored yellow for clarity) also superimpose closely. The orientation here is similar to the orientation of the A33 monomer on the right in Fig. 1A. CTLDs that have been found to be homodimers were chosen for comparison. (B) The view is rotated toward the viewer and to the left about 45° in order to see the “long loop.” Each of the five CTLDs has the “long loop” connecting the β2 and β3 strands, but A33 does not. Instead, A33 has a short connecting loop (residues 155 to 157). The legend to Fig. 3 identifies the five structures from which monomer CTLDs were extracted and superimposed on the A33 monomer.