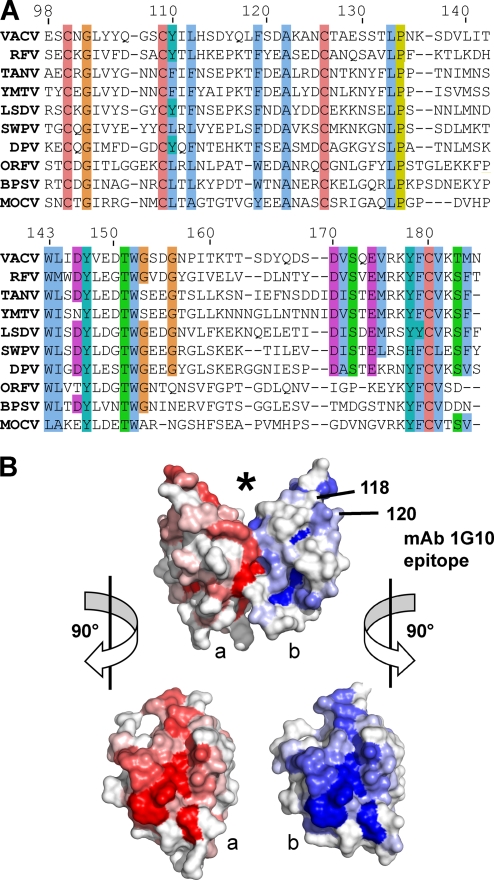
FIG. 5.
The A33 dimer interface is conserved in the Chordopoxvirinae subfamily. (A) The top line is the sequence of A33 from vaccinia virus (VACV) in the structure described herein. The A33 sequence is aligned with the sequences of nine A33 orthologs: RFV (rabbit fibroma virus), TANV (tanapox virus), YMTV (yaba monkey tumor virus), LSDV (lumpy skin disease virus), SWPV (swinepox virus), DPV (deerpox virus), ORFV (orf virus), BPSV (bovine papular stomatitis virus), and MOCV (molluscum contagiosum virus). Sequence similarities have been shaded with the ClustalX color scheme. Cysteines for the C100-C109 and C126-C180 disulfides are completely conserved. (B) Surface representation of A33 with the molecule in the same view as in Fig. 1. The location of the putative ligand binding site is marked (*). The location of the surface implicated in the MAb 1G10 epitope and contributed by residues 118 and 120 is indicated on the “b” monomer (blue). Monomers “a” and “b” have been shaded red and blue, respectively, accordingly to the sequence conservation at that position in the alignment in panel A. A bright red or blue patch means that a high percentage of the sequences in panel A have the same residue as does vaccinia virus A33 at that position. The alignment in panel A was used as input to the ProtSkin server (12). Residues 118 and 120 of the “a” monomer (red) are not visible in this view. GenBank geninfo identifiers (gi) are as follows: VACV, 66275953; RFV, 9633931; TANV, 157939746; YMTV, 38229285; LSDV, 15150561; SWPV, 18640205; DPV, 62637509; ORFV, 32167503; BPSV, 41018861; MOCV, 9629074. The sequence of the squirrelpox virus A33 ortholog (SQV) (88769957) is not shown for clarity, due to an eight-residue insertion between 141 and 142 and a six-residue insertion between residues 160 and 161.