Figure 5. Knocking down Hif1α completely rescues the metabolic phenotype in SIRT6 deficient cells.
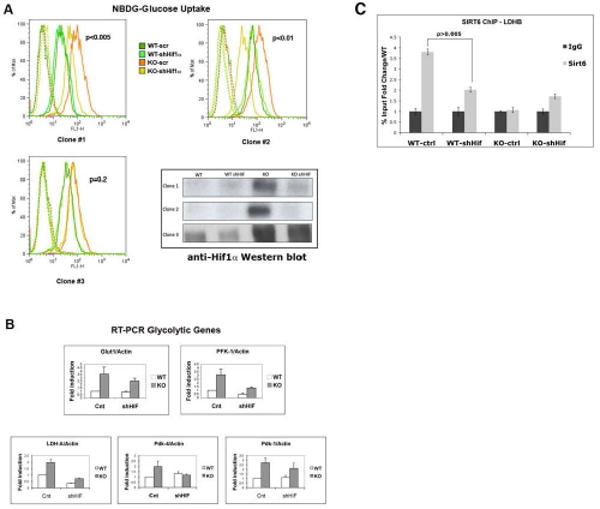
(A) SIRT6 WT and KO ES cells were infected with either a Hif1α-knockdown lentivirus (shHiflα) or vector alone (scr). Independent clones were expanded, and glucose uptake was measured using NBDG, as described before. Lower right panel: Western blot analysis of the different clones with an anti-Hif1α antibody. Note that clone #3 failed to down-regulate Hif1α, and thus it served as an internal control. (B) RNA was purified from Hif1α-KD clones and glycolytic gene expression levels were examined by RT-PCR. The different analyzed genes are indicated. Fold induction was normalized against actin. Three independent samples were averaged, keeping a threshold of 0.4 as confidence value in the threshold cycle (Ct). Error bars in all graphs indicate the standard error of the mean. (C) Hif1α recruits SIRT6 to the glycolytic promoters. ChIP was performed on wild-type control (WT-ctrl) and Hif1α knock-down cells (WT-shHif) with an antibody against SIRT6. Real-time PCR were carried out using primers specific for the promoter region of the LDHB gene. SIR6 KO cells were used as negative controls in the ChIP assay.
